Let’s get one thing straight—robotic process automation in healthcare isn’t about replacing clinicians with bots. It’s about giving burned-out staff their evenings back and making administrative chaos…less chaotic.
In a sector plagued by outdated systems and paperwork purgatory, medical RPA is quietly becoming the backbone of digital health operations. From scheduling to claims to population health reporting, healthcare organizations are leveraging this technology not for novelty—but for survival.
As AI and automation mature, we’re not just automating clicks—we’re reshaping patient care, transforming medical records workflows, and finally giving humans more time to do human things. And in 2025, that’s not a nice-to-have—it’s oxygen.
Key Takeaways
- RPA for healthcare isn’t just about cost savings—it’s about reclaiming time.
Health systems are using bots to automate tedious tasks like claims processing, prior auth submissions, and scheduling. The result? 700–980 hours saved per staffer annually and burnout metrics trending in the right direction. - Robotic process automation for healthcare now plays a central role in modernizing legacy workflows.
Whether it’s integrating with EHRs, streamlining patient intake, or improving billing accuracy, RPA is no longer a sidekick—it’s core infrastructure in the digital health ecosystem. - Knowing when to deploy RPA—and when not to—is critical.
RPA isn’t a hammer for every nail. When applied strategically, it transforms outcomes. When misapplied, it just adds technical debt. Successful implementations hinge on governance, orchestration, and frontline buy-in.
Table of Contents
- What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare?
- 7 Ways Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare Slashes Costs and Burnout
- High-Impact RPA in Healthcare Use Cases You Can Deploy Today
- Common Pitfalls of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare Projects
- A Pragmatic Roadmap for RPA Implementation in Healthcare—From Pilot to Enterprise Scale
- The Future of RPA in Healthcare—Hyper-Automation, Gen-AI Copilots and Digital Workers
- Why Choose Topflight for Healthcare RPA Solutions
What is Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare?
If you’ve spent more than a minute navigating healthcare’s administrative labyrinth, you already know it’s crying out for help—preferably robotic. So, exactly what is RPA in healthcare?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) isn’t the sci-fi scenario of actual robots roaming hospital corridors (though we’d all love to see that). Instead, it’s about software bots that handle the tedious, repetitive tasks no one likes—claim submissions, patient registrations, and compliance audits—with ruthless efficiency and zero coffee breaks.
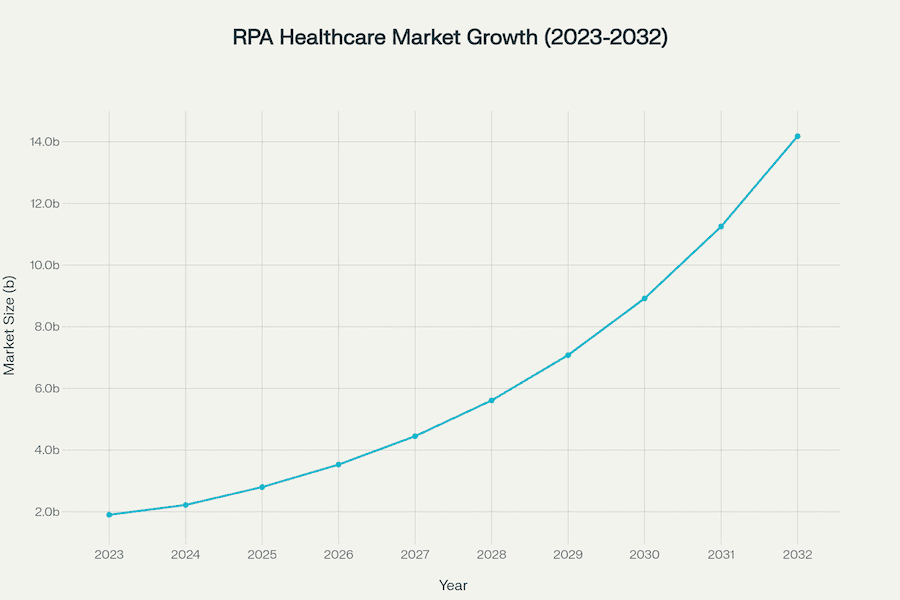
The healthcare industry has hit a tipping point, realizing automation isn’t a luxury—it’s survival. In fact, RPA adoption is skyrocketing, fueled by an explosive market expansion projected to jump from $0.67 billion in 2024 to nearly $7 billion by 2034 in the U.S. alone, clocking an impressive 26.31% CAGR. Globally, we’re looking at a leap from $1.9 billion in 2023 to over $14 billion by 2032.
Clearly, bots are big business because healthcare finally figured out it’s cheaper, faster, and smarter to automate routine tasks and let humans do what they’re best at—caring for patients.
Today, RPA bots handle tasks with strict rules—think claims processing, scheduling appointments, billing, and compliance reporting—with stunning accuracy. Organizations already report reductions of up to 80% in claims processing times, and 85% fewer data entry errors. With results like that, it’s no wonder healthcare is doubling down on digital workers to boost productivity, slash operational costs, and improve patient experiences.
This shift reflects broader trends in digital health: leveraging RPA capabilities for smarter data management, less burnout, and better care coordination.
For a broader view of how automation transforms healthcare operations, see What Is Automation in Healthcare.
7 Ways Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare Slashes Costs and Burnout
When it comes to healthcare, the biggest headache isn’t always clinical—it’s administrative. Enter robotic process automation in healthcare. Let’s talk brass tacks about how RPA directly impacts operational bottom lines and workforce well-being.
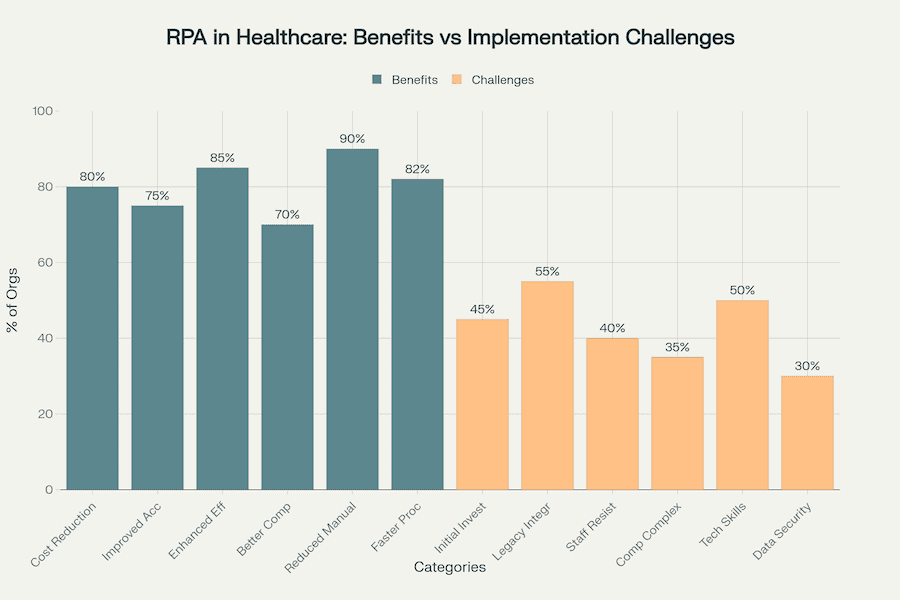
RPA implementation in healthcare: Benefits reported by 70-90% of organizations vs. challenges faced by 30-55%
Drastic Cost Reduction
Organizations deploying RPA consistently see substantial financial gains, with up to 80% reporting major cost reductions. For example, APDerm, a large dermatology practice partnering with athenahealth, achieved $400,000 in annual savings by automating claims processing, improving their clean claim rate by 47%.
Operational Efficiency
Imagine processing times getting chopped down by up to 300%. A recent lean digital transformation case documented a staggering 380-minute reduction per medical expense claim after introducing RPA. Such bots tirelessly complete tasks after hours and on weekends, without overtime pay, boosting throughput dramatically.
Claims Processing Acceleration
Claims handling—the bane of every billing department—sees up to an 80% speed improvement. Healthcare automation leader AKASA highlights that claim-status checks, previously taking human agents eight minutes each, can be executed by RPA in mere seconds.
Improved Accuracy and Compliance
Accuracy isn’t a luxury in healthcare—it’s critical. RPA reduces data-entry errors by around 85%, with billing accuracy improving by approximately 90%. Fresno Community Health Network exemplifies this, seeing a 22% decrease in prior authorization denials after implementing an RPA solution.
Reducing Staff Burnout
Staff freed from repetitive tasks report lower burnout levels. Deloitte’s 2024 findings reveal that RPA saves 700-870 hours annually per scheduler, and even more (810-980 hours) per claims-processing professional, enabling teams to refocus on patient-centric activities.
RPA’s impact is amplified when paired with artificial intelligence—RPA and AI together unlock a new layer of intelligent workflow automation. It’s not just routine execution; it’s cognitive support for frontline staff.
Scalability Without Staffing Costs
RPA lets healthcare organizations scale rapidly without proportional headcount increases. For instance, Avera Health saved $260,000 in employee-related expenses by deploying RPA bots for managing claims statuses and account verification processes.
Legacy System Relief
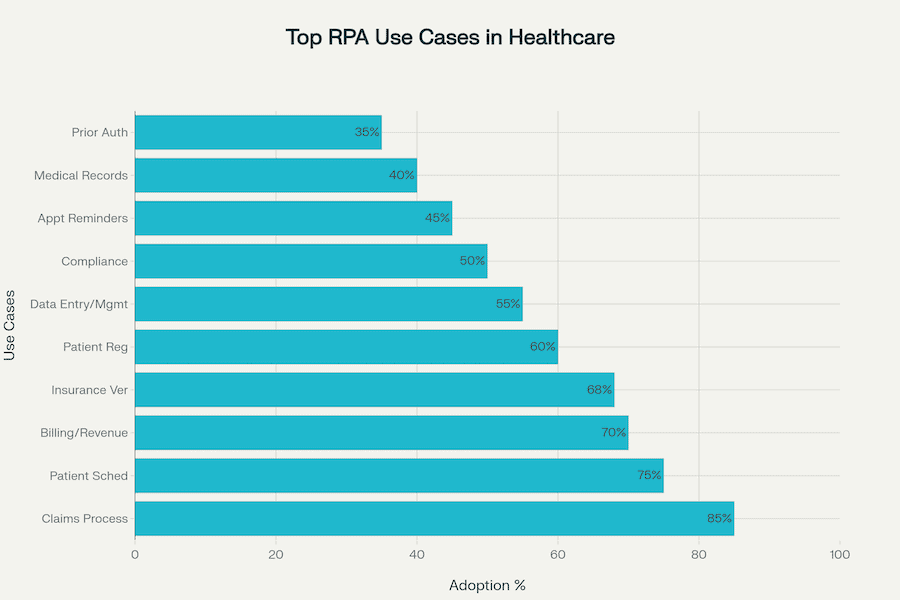
Despite integration hurdles, RPA effectively bridges gaps left by outdated legacy systems, rejuvenating them without costly replacements, as demonstrated by widespread adoption rates for patient scheduling (75%) and insurance verification (68%).
These results align with the growing demand for healthcare workflow automation software that integrates seamlessly with legacy systems.
Ultimately, these real-world examples underline the RPA benefits: healthcare robotic process automation healthcare solutions not only cut costs—they fundamentally enhance healthcare delivery, giving clinicians and staff renewed bandwidth to reconnect with their primary purpose: caring for patients.
High-Impact RPA in Healthcare Use Cases You Can Deploy Today
If you’re looking for high-impact automation plays in healthcare, follow the money—straight into the revenue cycle. Across major EHR platforms like Epic, Cerner, and Athena, RPA has proven to be less a moonshot and more a microwave: fast ROI, quick deployments, and immediate relief where operations bleed most.
1. Revenue Cycle Automation: Where the ROI Is Already Documented
Cleveland Clinic saw $700,000 in ROI over 3 years by automating patient registration and claim edits inside Epic, cutting processing time by 80%. APDerm, an Athenahealth user, saved $400,000 annually just by automating Tax ID number selection for claims—a tweak that also improved their clean claim rate by 47% and cut Days in AR by 20%.
Cerner clients like Northwell Health scaled to 2,500 patients billed nightly during COVID vaccine administration, while another Tennessee system reduced RCM accounting errors from 30% to 2% and freed 32 hours per week through transaction processing automation.
2. Patient Access: Automating the “Front Door”
A large U.S. medical center deployed an Epic-integrated RPA bot in just 48 hours to support COVID drive-through test registration. Processing time per patient dropped from 2–3 minutes to just 14–16 seconds, with bots eliminating routing errors that had caused six-hour wait times.
Cerner implementations also support scheduling at scale: one health system used RPA to migrate 12,418 appointments in weeks—something that had taken 12 staffers working nights and weekends the year before.
3. Clinical Documentation and CDI: Cutting Admin Overhead
At Michigan Medicine, Epic-integrated hospital RPA bots now automate hospital and professional billing plus anesthesia coding—saving 184 staff hours monthly across tasks like secondary claims, EKG ID, and data transcription between systems.
Related: Medical Document Automation Guide
While not clinical in the diagnostic sense, these automations touch key parts of CDI pipelines—ensuring faster, cleaner documentation flows without manual double entry.
4. Supply Chain and Inventory (The Quiet Hero Use Case)
Although the mentioned cases don’t center on inventory, the same Cerner bots that migrate scheduling data and manage vaccine billing could just as easily handle recurring supply-chain entries, restock alerts, and PO verification.
In similar implementations, RPA has shown success reducing reorder errors and accelerating materials management workflows.
5. Population Health and Quality Reporting (Underutilized, High Potential)
Many of the most powerful pop-health reporting opportunities remain untapped—despite the clear value of bots in pulling structured data from EHRs to generate CMS-quality metrics or registry submissions. Michigan’s cross-system transcription bots already hint at what’s possible: accurate, cross-platform data migration that forms the foundation for reporting that doesn’t eat up analyst time.
Across the board, these aren’t hypothetical gains—they’re real, repeatable, and increasingly plug-and-play. Time savings of 25,000+ hours/year, error drops from 30% to 2%, and implementations as fast as 48 hours prove that robotic process automation for healthcare has moved from “proof of concept” to “business as usual.”
While this blog focuses on software bots, automation also plays a crucial role in physical tools. Just consider the surge in medical devices used in clinical trials where RPA can coordinate data collection, synchronization, and trial logistics.
Common Pitfalls of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare Projects
Yes, RPA for healthcare can deliver big wins—but when it fails, it fails hard. Behind the glossy ROI reports are some sobering lessons from real-world misfires. Let’s unpack the most common failure modes, what causes them, and what happens when they go unchecked.
1. Bot Sprawl and Orphaned Scripts: The Shadow Army Problem
One U.S. healthcare organization discovered 28% more bots active than they had officially documented—many built by end-users or consultants without IT’s knowledge. These “shadow bots” were performing critical tasks with no oversight, logging, or fallback plans. The result? Audit chaos, compliance risk, and zero accountability when something broke.
Outcome: Untracked automations consumed resources and quietly undermined the very efficiency they were meant to create.
2. Change Management Nightmares: When the Workflow Rejects the Bot
Mayo Clinic’s IBM Watson–powered clinical trial matching system sounded brilliant on paper. But it flopped in its initial rollout. Why? Providers simply didn’t adopt it—it didn’t fit their workflow. Only after adding dedicated clinical coordinators to screen matches did trial enrollment pick up.
Outcome: The tool was technically accurate but practically unusable until workflows were redesigned—an expensive and time-consuming pivot.
3. Fragile Automations and Cost Overruns: When Bots Break Under Pressure
Healthcare revenue cycle automation teams have learned the hard way: even minor UI tweaks (a redesigned payer portal or a new EHR version) can break bots overnight. One RCM leader summed it up: “Our automation is like a house of cards.” A mid-sized payer reported that infrastructure and compliance overheads exceeded licensing fees by 300%, and had to hire full-time staff just to babysit medical RPA bots.
Outcome: Projects built to save money ended up inflating budgets—fast.
4. Precision Gone Wrong: Rigid Logic, Real-World Chaos
Solv Health deployed an RPA bot to transfer patient data into EMRs across partner clinics. But the bot’s matching logic was too strict, leading to duplicate patient charts—a clinical and compliance risk. Two clinics shut the bot down entirely. Reconciliation costs per chart ran between $50–96, and one clinic even threatened to abandon the platform.
Outcome: Automation intended to reduce admin work did the opposite—triggering manual cleanups, operational frustration, and customer churn risk.
RPA doesn’t fail because the tech is bad—it fails when governance is loose, workflows are ignored, or complexity is underestimated. Every bot is a process decision made permanent. Make the wrong decision, and you’ve automated the wrong thing—at scale.
Before you scale RPA, pressure-test these three questions:
- Is your automation built to survive version changes, not just today’s UI?
- Have frontline users been involved—or are you automating in a vacuum?
- Who owns each bot, and who’s on call when it fails at 2 a.m.?
Ignore these, and you’re not scaling automation—you’re scaling fragility. Without clear governance, even a well-intentioned RPA application can spiral into technical debt. The role of services like change management, version control, and user feedback loops cannot be overstated.
A Pragmatic Roadmap for RPA Implementation in Healthcare—From Pilot to Enterprise Scale
Let’s be blunt: most RPA projects in healthcare don’t fail because of bad tech—they fail because someone tried to run before they could automate walking. If you’re serious about getting real ROI, you need more than a license key and a use case. You need a rollout plan with teeth.
Step 1: Start Small—But Start Where It Hurts
The fastest wins come from high-volume, rules-based tasks with measurable pain. Think claims status checks, denial workflows, or prior auth routing. As already mentioned, APDerm achieved $400,000 in annual savings and a 47% clean claim rate boost by automating Tax ID selection. That wasn’t a moonshot—it was a single, repetitive decision that RPA now handles perfectly, 24/7.
Step 2: Quantify the Win—Minutes Saved → Dollars Earned
Let’s do the math:
- One manual claim check = ~8 minutes (AKASA)
- RPA does it in seconds
- 1,000 claims/day = 130+ hours saved weekly
- Multiply by fully loaded FTE cost = serious money
Deloitte pegs annual savings at 810–980 hours per claims-processing staffer. That’s not a rounding error—it’s budget you can reallocate to hiring, tech upgrades, or burnout mitigation.
Step 3: Build-vs-Buy-vs-Outsource
- Build if you’ve got a DevOps dream team and appetite for long-term ownership
- Buy if you’re adding modular RPA to existing workflows (e.g., UiPath, Power Automate)
- Outsource if your internal IT is already underwater—partner with RPA integrators who know HIPAA and EHR complexity cold
Step 4: Govern Like It’s a Real Product
Even simple bots need monitoring, rollback plans, and change logs. Build an internal RPA Center of Excellence (CoE) or at least assign ownership. Otherwise, today’s MVP becomes tomorrow’s orphaned script graveyard.
Step 5: Scale Only After Repeatable Success
Once your first bot pays for itself (usually within 12–18 months), rinse and replicate. Remember how Avera Health saved $260,000 annually just by automating account verification and claims queueing? Multiply that playbook across departments and you’ve got enterprise-scale momentum.
Bottom line: Don’t treat medical RPA as a tech pilot. Treat it as an operational capability—with pipelines, governance, and ROI accountability baked in from day one.
The Future of RPA in Healthcare—Hyper-Automation, Gen-AI Copilots and Digital Workers
As current usage of RPA in healthcare matures, we’re seeing it evolve into something more than just automation—it’s acquiring strategic meaning across digital health ecosystems. The next chapter? Hyper-automation.
In 2025, RPA is no longer just about automating discrete tasks. It’s about combining RPA with Large Language Models (LLMs), AI agents, low-code tools, and process mining to orchestrate entire workflows—turning bots into teammates and interfaces into action surfaces.
From Rules to Reason: RPA + AI + LLM = Cognitive Automation
Healthcare isn’t just swimming in data—it’s drowning in unstructured clinical notes, scanned PDFs, and payer correspondence. That’s where artificial intelligence step in. Combined with RPA, LLMs power digital workers that not only read and interpret messy data but also reason across steps.
Imagine an AI driven RPA that:
- Parses a referral note,
- Extracts diagnosis + authorization needs,
- Submits to the payer portal, and
- Updates the EHR with the outcome.
This isn’t speculative. Health systems like AtlantiCare and St. Luke’s are already using ambient LLM scribes to reclaim 60+ minutes per clinician per day—eliminating manual note-taking altogether.
At Topflight, we’ve seen this firsthand with GaleAI, a medical coding assistant that uses LLMs to extract structured billing codes from unstructured clinical inputs. While GaleAI doesn’t use RPA per se—it connects via API—it shows how AI can handle fuzzier, context-rich tasks that traditional bots can’t. Pair that automated medical billing with RPA, and you’ve got a digital workforce that doesn’t just automate clicks—it makes judgment calls.
Ambient and Agentic: UI Automation Goes Fully Autonomous
Traditional bots break when the UI changes. Agentic AI solves this: it sees the screen (via computer vision), understands what to do (via an LLM), and acts like a human—clicking, typing, adapting. This allows automation even in systems without APIs (hello, legacy EHRs).
Enterprise Automation Becomes a Fabric
Leading orgs are moving from one-off bots to system-wide automation platforms. This means layering automation as an enterprise operating system, not just a series of scripts. Think process mining for prioritization, LLMs for cognition, and low-code builders for democratized bot creation.
Cloud Delivery and Accessibility
With Hyper-automation-as-a-Service (HaaS), smaller providers can now tap into what used to be enterprise-only tech—without shelling out six figures up front. Robot-as-a-Service platforms bring automation to clinics, not just health systems.
The Catch? Governance
With great AI power comes great audit trails. Hyper-automation without oversight is a HIPAA nightmare. “Human in the loop” is non-negotiable. So are secure BAAs, role-based access, and LLM validation layers.
The future of RPA in healthcare isn’t about bots doing tasks faster—it’s about building a digital workforce that collaborates with the human one. Hyper-automation isn’t just scaling operations—it’s reshaping what healthcare delivery looks like.
Why Choose Topflight for Healthcare RPA Solutions
We won’t pretend to have a bot army clicking through payer portals in the basement—but we know when, where, and why to deploy RPA in healthcare, and more importantly, when not to. That’s what makes Topflight valuable: we’re not an RPA vendor—we’re your strategic integration partner, fluent in both APIs and automations.
Here’s how we help healthcare orgs de-risk RPA and get it right from day one:
- Right Tech, Right Use Case.
We’ve advised on dozens of integration projects where the real decision wasn’t how to build it—but what to build. FHIR APIs, HL7, vendor SDKs, or RPA? We assess workflows, system access limitations, and compliance exposure to make an informed recommendation—not a default to code or bot. - Hybrid Automation That Works Together.
In the field, we’ve built API-driven modules that pull patient data and used light-touch automation to populate fields in a legacy billing UI. RPA isn’t all-or-nothing—it’s part of a modern orchestration stack. And we know how to stitch that stack together so humans aren’t left reconciling the seams. - Compliance and Vendor Navigation.
If RPA’s involved, we bake HIPAA compliance into the design: encrypted vaults, activity logs, audit-friendly documentation. And when an EHR vendor needs to be looped in (say, for guidance on automation boundaries), we speak their language. Our engineers have worked across Epic, Cerner, Athena, Canvas, and others. - Future-Proof Support.
Whether it’s maintaining an integration post-go-live or updating a bot that broke due to an EHR UI tweak, we’re in for the long haul. Think of us as your integration command center—available when workflows shift, requirements change, or systems evolve.
Related: HIPAA Compliant App Development Guide
At Topflight, we build working automations, not science projects. That means knowing when healthcare robotic process automation is the tool—and when it’s just a crutch. We help you pick the right approach, prove it fast, and scale it responsibly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of robotic process automation in healthcare?
RPA reduces costs, accelerates workflows, improves accuracy, and decreases staff burnout. It handles repetitive administrative tasks, allowing human staff to focus on patient care.
What is robotic process automation (RPA) in healthcare?
RPA in healthcare refers to software bots that automate rule-based, repetitive processes—like claims processing, appointment scheduling, and billing—without requiring manual human intervention.
What are the most common use cases of RPA in healthcare?
Typical use cases include revenue cycle management, prior authorizations, patient registration, clinical documentation support, supply chain automation, and data migration between systems.
What challenges can arise when implementing RPA in healthcare?
Common pitfalls include bot sprawl, lack of workflow alignment, fragile automations prone to breaking after system updates, and compliance risks from shadow IT or poor governance.
How does RPA improve patient and staff experience in healthcare?
RPA reduces administrative burdens, shortens wait times, minimizes data entry errors, and frees up staff for more meaningful work—directly improving the experience on both sides of the care equation.