Imagine this: It’s 2 am, and you’re wide awake, feeling unwell. The doctor’s office is closed, and your symptoms aren’t severe enough to warrant a trip to the emergency room. What do you do?
This was the predicament Sarah, a 30-year-old graphic designer from Sydney, faced. She had been feeling under the weather for a few days, but it wasn’t until this sleepless night that she decided to seek help. Instead of waiting hours in an ER or for her GP’s office to open, Sarah turned to an unlikely source for medical advice – a chatbot.
Sarah’s experience with a medical chatbot was much more than she’d bargained for. Not only did the chatbot provide immediate, specific, and accurate information, but it also allowed her to express her concerns without judgment, no matter the hour. The chatbot’s empathetic responses and ability to guide her through a series of health-related questions left Sarah feeling heard, understood, and, most importantly, reassured.
In our increasingly digital world, Sarah’s story is becoming less of an exception and more of a norm. Medical chatbots are revolutionizing how we interact with healthcare, providing round-the-clock support, reducing errors, and enhancing patient-physician relationships. But how do these AI-powered platforms come to life?
And what goes into developing a chatbot that can deliver such a human-like, empathetic interaction?
Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of medical chatbot development, exploring how they’re transforming healthcare, one patient interaction at a time.
Table of Contents:
- The Advent of Medical Chatbots
- The Impact of Healthcare Chatbots
- Building a Medical Chatbot: Key Steps for Development
- Navigating HIPAA Compliance
- Addressing Bot Hallucinations
- Platform Recommendations
- Proper Redirection to Human Operators
- Top Medical Chatbots
- Why Topflight Nails Medical-Chatbot Builds
- Ready to Build Your Medical Chatbot?
Top Takeaways:
- Medical chatbots provide 24/7 support, offering immediate, non-judgmental medical advice, thus revolutionizing patient-doctor interactions.
- Compliance with HIPAA is a critical requirement when developing medical chatbots. You can ensure HIPAA adherence by anonymizing PHI, entering a BAA agreement with vendors, or self-hosting language models. Each method has pros and cons and requires careful consideration, significant resources, and technical expertise.
- Successfully mitigating chatbot hallucinations requires strategic use of verified external databases for context-appropriate responses, leveraging NLP semantic search techniques to ensure accuracy.
⚡️ For Our Time-Conscious Readers:
- How to ensure HIPAA compliance in my GPT medical chatbot? Insight 👇🏻
- What are the best ways to address AI bot hallucinations? Insight 👇🏻
- What are the best practices for Retrieval-Augmented Generation? Insight 👇🏻
- How do I make ChatGPT HIPAA compliant? Insight 👇🏻
- How to retrieve accurate patient info for my GenAI chatbot? Insight 👇🏻
The Advent of Medical Chatbots: A New Era in Healthcare
When it comes to redefining the future of healthcare, the time is ripe for innovative digital solutions. In 2023, propelled by technological advancements, there’s an inspiring momentum in medical automation, particularly with medical chatbots, as they become essential tools in reimagining healthcare.
From handling patient queries to appointment scheduling, medical chatbots are not mere add-ons but essential tools in modern healthcare management.
Driven by the power of Artificial Intelligence (AI), these chatbots are more than just digital receptionists; they’re sophisticated administrative partners. Investment in healthcare AI, which powers not only telemedicine and remote patient monitoring (RPM) but also the transformative chatbots mentioned earlier, has seen exponential growth, and there’s no sign of this trend slowing down.
Fueled by such innovations, the global artificial intelligence in the healthcare market reached USD 15.4 billion in 2022, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.5% from 2023 to 2030.
The Impact of Healthcare Chatbots: Promising Changes and Practical Applications
Imagine the administrative workload of hospitals reduced by up to 73% (according to Insider Intelligence), thanks to intelligent chatbots taking over tasks like reminders, FAQs, and even triaging! That’s not a futuristic dream; it’s a reality many healthcare providers are beginning to embrace. According to a Tebra survey of 500 health care professionals, 10% of healthcare providers already use AI in some form, and half of the remaining 90% plan to use it for data entry, appointment scheduling, or medical research.
But why stop there? Medical chatbots are also breaking barriers in patient engagement. The days of patients waiting on hold or struggling to find the correct information online are fading away. Medical chatbots optimize administrative processes and revolutionize patient experiences, allowing for smoother, more personalized interactions.
Here’s a glimpse of what medical chatbots have managed to achieve:
- Streamlining Appointments: Forget the endless back-and-forth emails and calls; chatbots can schedule appointments in seconds.
- 24/7 Patient Support: Whether it’s 2 am or 2 pm, chatbots are always there to answer questions, providing real-time support.
- Enhancing Patient Engagement: Personalized reminders, follow-ups, and information dissemination have never been so effortless.
- Cutting Costs: By automating routine tasks, chatbots allow healthcare staff to focus on more critical areas, reducing operational costs.
But the journey to medical chatbot excellence is not without challenges. Navigating HIPAA compliance, addressing potential hallucinations, choosing the right platform, and ensuring proper human assistant redirection are complex yet vital aspects of medical chatbot development.
Whether you’re a healthcare provider aiming to enhance patient care or a tech-savvy entrepreneur eyeing the burgeoning healthcare AI market, understanding the dynamics of medical chatbots is essential.
It’s not just about riding the wave of digital transformation; it’s about steering the ship toward a brighter, more responsive healthcare landscape.
Dive in, and let’s explore the promising world of medical chatbots together.
Building a Medical Chatbot: Key Steps for Development
Designing a healthcare chatbot isn’t just about coding—it’s about crafting a seamless, human-like experience that patients and providers can trust. Follow these steps to create an intuitive, HIPAA-compliant chatbot that truly understands and engages users.
Step 1: Design the Conversation Pathway
Long before AI-powered chatbots, human conversations naturally followed structured yet fluid pathways. Whether speaking in person, over the phone, or through messaging apps, effective communication relies on shared rules—clarity, responsiveness, and intent. These same principles apply when designing chatbot interactions, especially in healthcare, where accuracy and empathy are crucial.
A well-designed conversational experience isn’t just about giving users answers; it’s about guiding them through an intuitive, natural dialogue. A chatbot should anticipate user needs, recognize intent, and maintain a conversational flow that mirrors human interaction. This means applying principles of cooperation, context awareness, and turn-taking—elements that make communication productive in real-world settings.
For healthcare applications, the stakes are even higher. A patient asking a medical question isn’t looking for a generic definition—they need actionable, relevant guidance. If the chatbot fails to acknowledge intent, misinterprets context, or delivers an overwhelming information dump, it risks frustrating the user rather than helping them. This is why designing an effective conversational flow requires careful attention to how humans naturally interact, ensuring that AI-driven responses feel helpful, contextual, and engaging.
Conversational cooperation and intent
Before designing a conversational pathway for an AI driven healthcare bot, one must first understand what makes a productive conversation. One of these principles is the principle of cooperation.
As phrased by Philosopher Paul Grice in 1975, the principle of cooperation holds that a conversation between two or more persons can only be useful if there is an underlying contextual agreement or cooperation. This background advances the conversation in an agreed direction and maintains the proper context to achieve a common purpose.
For instance, take this conversation.
John: Do you have an idea what books I should read for this exam?
Greg: Yes, I do.
In this example, Greg does not adhere to the principle of cooperation. This is because his response does not answer John’s question: it leaves John with literally no answers to his question, hence a conversational disagreement.
Although literally asking if Greg knew any books needed for the exam, John’s question was not intended as a yes-or-no question. John was indeed asking to know the books he needed for the exam, and Greg did not provide that.
The same goes for this conversation with a healthcare chatbot.
User: What do I do if my newborn’s eyes have become yellow?
Bot: Yellow discoloration of the eyes is called Jaundice, and it is caused by excess bilirubin…
While it is true that yellow discoloration of the eyes (and skin) is known as jaundice, the bot does not answer the user’s question.
In designing an adequate conversational flow for a medical chatbot app, therefore, understanding intent is vital. Chatbot developers can employ Natural Language Understanding (NLU) platforms such as Google Dialogflow, IBM’s Watson, Facebook’s wit.ai, Amazon’s Lex, and Microsoft Cognitive Services Language Understanding LUIS.ai.
These platforms match utterances and their variants with appropriate intents before generating responses. This maintains natural and free-flowing conversations between the user and the chatbot.
Context
Just as effective human-to-human conversations largely depend on context, a productive conversation with a chatbot also heavily depends on the user’s context.
This leads to one of the most important elements of a conversational pathway: Defining your audience. This requires extensive research into who your audience is, their problems and needs, how they want their problems solved, the appropriate language to use for them, and their socio-economic contexts.

You do not design a conversational pathway the way you perceive your intended users, but with real customer data that shows how they want their conversations to be. Fortunately, chatbots for healthcare can mimic various personalities.
A drug bot answering questions about drug dosages and interactions should structure its responses for doctors and patients differently. Doctors would expect essential info delivered in the appropriate medical lexicon.
Similarly, conversational style for a healthcare bot for people with mental health problems such as depression or anxiety must maintain sensitivity, respect, and appropriate vocabulary.
For instance:
User: My panic symptoms have been getting more frequent recently, how do I resolve this?
Bot: It appears you might not have been using your medications correctly.
While this may be correct, it comes off as an insensitive response for a user with an anxiety disorder. Furthermore, it may not be accurate at all, as there may be other factors predisposing the user to frequent panic attacks.
Identifying the context of your audience also helps to build the persona of your chatbot. The chatbot persona gives a human feel to these conversations. A chatbot persona embodies the character and visual representation of a chatbot.
For example, for a doctor chatbot, an image of a doctor with a stethoscope around his neck fits better than an image of a casually dressed person. Similarly, a picture of a doctor wearing a stethoscope may fit best for a symptom checker chatbot. This relays to the user that the responses have been verified by medical professionals.
The character of a chatbot also depends on the context of the audience. A friendly and funny chatbot may work best for a chatbot for new mothers seeking information about their newborns. Still, it may not work for a doctor seeking information about drug dosages or adverse effects.
Just as patients seeking information from a doctor would be more comfortable and better engaged by a friendly and compassionate doctor, conversational styles for chatbots also have to be designed to embody these personal qualities.
Turn-taking
One of the key elements of an effective conversation is turn-taking, and many bots fail in this aspect.
Here’s one of the examples used above.
User: My newborn’s eyes have become yellow, what do I do?
Bot: Yellow discoloration of the eyes is called Jaundice, and it is caused by excess bilirubin in the bloodstream, which may result from excess production of bilirubin from the breakdown of red blood cells or accumulation of bilirubin due to obstruction in its flow pathway. Jaundice is…
The chatbot goes on and on describing jaundice and leaves no space for the user to respond. Good communication flow involves switching the conversation: allowing the user and the chatbot to take turns in speaking.
Not only do these responses defeat the purpose of the conversation, but they also make the conversation one-sided and unnatural.
This concept is described by Paul Grice in his maxim of quantity, which depicts that a speaker gives the listener only the required information, in small amounts. Doing the opposite may leave many users bored and uninterested in the conversation.
Now that you have understood the basic principles of conversational flow, it is time to outline a dialogue flow for your chatbot. This forms the framework on which a chatbot interacts with a user, and a framework built on these principles creates a successful chatbot experience whether you’re after chatbots for medical providers or patients.
Step 2: Select the Optimal UI
Chatbots are revolutionizing social interactions on a large scale, with business owners, media companies, automobile industries, and customer service representatives employing these AI applications to ensure efficient communication with their clients.
Also, check out our guide about AI app development.
However, humans rate a process not only by the outcome but also by how easy and straightforward the process is. Similarly, conversations between men and machines are not nearly judged by the outcome but by the ease of the interaction. That’s where a thought-out User Interface (UI) comes in.
A user interface is the meeting point between men and computers; the point where a user interacts with the design. Depending on the type of chatbot, developers use a graphical user interface, voice interactions, or gestures, all of which use different machine learning models to understand human language and generate appropriate responses.
Popular platforms for developing chatbot UIs include Alexa API, Facebook Messenger, Skype, Slack, Google Assistant, and Telegram.
These platforms have different elements that developers can use for creating the best chatbot UIs. Almost all of these platforms have vibrant visuals that provide information in the form of texts, buttons, and imagery to make navigation and interaction effortless.
All these platforms, except for Slack, provide a Quick Reply as a suggested action that disappears once clicked. Users choose quick replies to ask for a location, address, email, or simply to end the conversation.
Some of these platforms, e.g., Telegram, also provide custom keyboards with predefined reply buttons to make the conversation seamless.
Each of these platforms has unique merits and disadvantages. So choosing the right platform may seem daunting. However, let these simple rules guide you for selecting the best UI for your chatbot:
- Make UI elements perform predictably, so users can easily navigate through the platform.
- Let elements be clearly labeled and indicated to improve usability.
- Design layout to improve readability: Ways to do this include avoiding excessive colors and buttons and using fonts, capitals, letters, and italics appropriately.
- Avoid numerous tasks on a single page. This can wear the user out and cause a lot of confusion. Restrict the number of tasks to one per page. Furthermore, complex tasks should be divided into subtasks to improve the usability of the bot.
- Finally, make the design simple to navigate.
An effective UI aims to bring chatbot interactions to a natural conversation as close as possible. And this involves arranging design elements in simple patterns to make navigation easy and comfortable.
Step 3: Blend Human Expertise with AI
When customers interact with businesses or navigate through websites, they want quick responses to queries and an agent to interact with in real time. Inarguably, this is one of the critical factors that influence customer satisfaction and a company’s brand image (including healthcare organizations, naturally). With standalone chatbots, businesses have been able to drive their customer support experiences, but it has been marred with flaws, quite expectedly.
For example, it may be almost impossible for a healthcare chat bot to give an accurate diagnosis based on symptoms for complex conditions. While chatbots that serve as symptom checkers could accurately generate differential diagnoses of an array of symptoms, it will take a doctor, in many cases, to investigate or query further to reach an accurate diagnosis.
In emergency situations, bots will immediately advise the user to see a healthcare professional for treatment. That’s why hybrid chatbots – combining artificial intelligence and human intellect – can achieve better results than standalone AI powered solutions.
GYANT, HealthTap, Babylon Health, and several other medical chatbots use a hybrid chatbot model that provides an interface for patients to speak with real doctors. The app users may engage in a live video or text consultation on the platform, bypassing hospital visits.
Step 4: Implement Rasa NLU for Smarter Chatbots
For an effective chatbot application and enjoyable user experience, chatbots must be designed to make interactions as natural as possible; and this requires machine learning models that can enable the bot to understand the intent and context of conversations. This is where natural language processing and understanding tools come in.
Rasa NLU is an open-source library for natural language understanding used for intent classification, response generation and retrieval, entity extraction in designing chatbot conversations. Rasa’s NLU component used to be separate but merged with Rasa Core into a single framework.
The NLU is the library for natural language understanding that does the intent classification and entity extraction from the user input. This breaks down the user input for the chatbot to understand the user’s intent and context. The Rasa Core is the chatbot framework that predicts the next best action using a deep learning model.
In this article, we shall focus on the NLU component and how you can use Rasa NLU to build contextual chatbots. Before going further, you must understand a few keywords.
Intent: This describes exactly what the user wants.
Take this example:
“Where can I buy Insulin in Denver, Colorado?” In this statement, the “intent” will be: buy_insulin.
Entity: An entity is a useful unit of data that provides more information about the user’s intent. The entity answers the questions “when” and “where” about the user’s intent.
In the above example, the entities will be: “location”: “Denver”, “Pharmacy”.
To build this structure for a conversational chatbot using Rasa, here are steps you should take:
- Installation and setup
- Training and testing
Installation and setup
The first step is to set up the virtual environment for your chatbot; and for this, you need to install a python module. Once this has been done, you can proceed with creating the structure for the chatbot.
Read Our Article about Python in Healthcare
Start by defining the pipeline through which the data will flow and the intent classification and entity extraction can be done. Rasa recommends using a spaCy pipeline, but several others, such as the supervised_embeddings pipeline, can be used.
To do this, activate the virtual environment and run this:
pip install rasaOnce this is completed, run the following command on your desired directory:
rasa init --no-promptThis will generate several files, including your training data, story data, initial models, and endpoint files, using default data.
You now have an NLU training file where you can prepare data to train your bot. You may use your own custom data with a markdown or JSON format. Open up the NLU training file and modify the default data appropriately for your chatbot.
Let’s create a contextual chatbot called E-Pharm, which will provide a user – let’s say a doctor – with drug information, drug reactions, and local pharmacy stores where drugs can be purchased. The first step is to create an NLU training file that contains various user inputs mapped with the appropriate intents and entities. The more data is included in the training file, the more “intelligent” the bot will be, and the more positive customer experience it’ll provide.
Related: How to build an e-pharmacy solution
See examples:
## intent: greet
– Hello
– Hey
– Hi there
– Good day
## intent: ask_Amoxicillin_dosage
– How is Amoxicillin taken?
– What’s the correct dose of Amoxicillin?
– How should I use Amoxicillin?
## intent: Amoxicillin_interactions
– Is Amoxicillin safe to use with Insulin?
– What are the likely interactions with Metformin?
– Which drugs react with Amoxicillin?
This data will train the chatbot in understanding variants of a user input since the file contains multiple examples of single-user intent.
To define entities and values, let’s use a previous example:
“Where can I buy Insulin in Colorado?”
The name of the entity here is “location,” and the value is “colorado.” You need to provide a lot of examples for “location” to capture the entity adequately. Furthermore, to avoid contextual inaccuracies, it is advisable to specify this training data in lower case.
You may design a lookup table containing a list of values for a single entity. This is preferable to creating sample sentences for all values.
For example, if a chatbot is designed for users residing in the United States, a lookup table for “location” should contain all 50 states and the District of Columbia.
Once you have all your training data, you can move them to the data folder. Ensure to remove all unnecessary or default files in this folder before proceeding to the next stage of training your bot.
Training and testing
To train the nlu mode, run this command:
rasa train nluThis command looks for training files in your data folder and creates a trained model. It then saves this model in the model folder. The model is named with a prefix nlu-, which indicates that it is a nlu-only type of model.
You can test a model by running this command:
rasa shell nluIf you want to test a single model out of multiple models, run this command:
rasa shell -m models/nlu-20190515-144445.tar.gzThis interactive shell mode, used as the NLU interpreter, will return an output in the same format you ran the input, indicating the bot’s capacity to classify intents and extract entities accurately.
The output will look something like this:
{'entities':[{'confidence':0.7756870940230542,
'end': 39,
'entity': 'location',
'extractor': 'ner_crf',
'start': 34,
'value': 'New York'}],
'intent': {'confidence': 0.7036955584872587, 'name': 'Pharmacy'},
'intent_ranking': [{'confidence': 0.7036955584872587, 'name': 'buy_drug'},
{'confidence': 0.08354613362606624, 'name': 'bye'},
{'confidence': 0.07291869896872455, 'name': 'fine_ask'},
'text': 'Where can I buy Insulin in New York?'}
After training your chatbot on this data, you may choose to create and run a nlu server on Rasa.
To do this, run this command:
rasa run --enable-api -m models/nlu-20190515-144445.tar.gzThe output it generates is modifiable to whatever parameters you choose. Once your server is running, you may test it using curl. This indicates the intent and confidence of your server.
That sums up our module on training a conversational model for classifying intent and extracting entities using Rasa NLU. Your next step is to train your chatbot to respond to stories in a dialogue platform using Rasa core. I shall explain this in subsequent articles.
Step 5: Ensure HIPAA Compliance
The Health Insurance and Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 is United States regulation that sets the standards for using, handling, and storing sensitive healthcare data. The act outlines rules for the use of protected health information (PHI).
The act refers to PHI as all data that can be used to identify a patient.
HIPAA considers the following data protected health information:
- Patient’s name, address, date of birth, and Social Security number
- A patient’s health status: this includes medical or mental health condition
- Any health service the patient has received or is currently receiving
- Information regarding the payment for healthcare services that could be used to identify the patient
Note: The HIPAA Privacy Rule does not consider employment and educational details as PHI. Furthermore, de-identified data – since it is not traceable to the owner of the data – does not fall under the HIPAA Privacy Rule.
Use Rasa stack
Rasa stack provides you with an open-source framework to build highly intelligent contextual models giving you full control over the process flow. Conversely, closed-source tools are third-party frameworks that provide custom-built models through which you run your data files. With these third-party tools, you have little control over the software design and how your data files are processed; thus, you have little control over the confidential and potentially sensitive patient information your model receives.
This is why an open-source tool such as Rasa stack is best for building AI assistants and models that comply with data privacy rules, especially HIPAA.
As long as your chatbot will be collecting PHI and sharing it with a covered entity, such as healthcare providers, insurance companies, and HMOs, it must be HIPAA-compliant.
Using these safeguards, the HIPAA regulation requires that chatbot developers incorporate these models in a HIPAA-complaint environment. This requires that the AI conversations, entities, and patient personal identifiers are encrypted and stored in a safe environment.
This involves all the pipelines and channels for intent recognition, entity extraction, and dialogue management, all of which must be safeguarded by these three measures.
With Rasa Stack, an open-source tool that runs under Apache 2.0 license, building a HIPAA-complaint chatbot is possible.
Rasa offers a transparent system of handling and storing patient data since the software developers at Rasa do not have access to the PHI. All the tools you use on Rasa are hosted in your HIPAA-complaint on-premises system or private data cloud, which guarantees a high level of data privacy since all the data resides in your infrastructure.
Furthermore, Rasa also allows for encryption and safeguarding all data transition between its NLU engines and dialogue management engines to optimize data security. As you build your HIPAA-compliant chatbot, it will be essential to have 3rd parties audit your setup and advise where there could be vulnerabilities from their experience.
Rasa is also available in Docker containers, so it is easy for you to integrate it into your infrastructure. If you need help with this, we can gladly help setup your Rasa chatbot quickly.
Administrative safeguards
The Security Rule defines administrative safeguards as all “administrative actions, policies, and procedures you need to set up to manage the implementation, development, and maintenance of security measures to protect health information and to manage the conduct of the covered entity’s workforce concerning the protection of that information.”
These safeguards include all the security policies you have put in place in your company, including designating a privacy official, to guide the use, storage, and transfer of patient data, and also to prevent, detect, and correct any security violations.
Physical safeguards
The Security Rule describes the physical safeguards as the physical measures, policies, and processes you have to protect a covered entity’s electronic PHI from security violations.
This safeguard includes designating people, either by job title or job description, who are authorized to access this data, as well as electronic access control systems, video monitoring, and door locks restricting access to the data.
Technical safeguards
These are the tech measures, policies, and procedures that protect and control access to electronic health data. These measures ensure that only authorized people have access to electronic PHI. Furthermore, this rule requires that workforce members only have access to PHI as appropriate for their roles and job functions.
Technical safeguarding involves the encryption of electronic PHI. The Rule requires that your company design a mechanism that encrypts all electronic PHI when necessary, both at rest or in transit over electronic communication tools such as the internet. Furthermore, the Security Rule allows flexibility in the type of encryption that covered entities may use.
The HIPAA Security Rule requires that you identify all the sources of PHI, including external sources, and all human, technical, and environmental threats to the safety of PHI in your company.
Navigating HIPAA Compliance
When it comes to the development of medical chatbots, a foundational principle that guides every decision is compliance with the Health Insurance and Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This crucial U.S. regulation establishes the criteria for managing, using, and storing sensitive healthcare information, including what falls under protected health information (PHI). Specifically, HIPAA refers to the following as PHI:
- Patient’s Personal Details: Name, address, date of birth, and Social Security number.
- Medical Information: Health status, including medical or mental health conditions.
- Healthcare Services: Details about the services the patient has received or is currently receiving.
- Payment Information: Any information regarding payment that could be used to identify the patient.
HIPAA’s domain doesn’t include employment and educational details or de-identified data, as these cannot be traced back to the individual.
Related: HIPAA-Compliant App Development Guide
Given the strict regulation, anyone developing these AI assistants handling PHI must be HIPAA-compliant. It’s not an option but a mandatory facet of healthcare app development.

HIPAA Compliance in Gen-AI Medical Chatbots
When implementing generative AI in healthcare applications, and medical chatbots in particular, it is crucial to adopt these key practices and tools to secure PHI:
- PHI Anonymization: Automatically strip out and reinsert PHI data after processing with generative AI models.
- Business Associate Agreements (BAAs): Ensure all third-party providers handling PHI sign BAAs to solidify their data protection responsibilities.
- Self-Hosted Large Language Models: Consider deploying self-hosted models to maintain control over data and ensure compliance.
- Out-of-the-Box Solutions: Utilize solutions like BastionGPT and CompliantGPT for automated PHI de-identification.
- Secure APIs: Leverage HIPAA-compliant APIs such as Amazon Comprehend Medical and Google Cloud Healthcare API to manage sensitive data securely.
- Data Encryption: Implement end-to-end encryption for data both at rest and in transit.
- Adhere to SOC-2 Principles: Follow SOC-2 guidelines to ensure administrative, physical, and technical safeguards.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Use multi-factor authentication to bolster security.
- Role-Based Access: Implement role-based access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel only.
- Audit Logging: Maintain detailed logs of data access and modifications for accountability.
- Remove PHI from Push Notifications: Ensure that push notifications do not contain any PHI to prevent accidental exposure.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can develop AI applications that uphold HIPAA standards and protect patient data effectively. Now, let’s spend a few extra minutes on each of these.
PHI anonymization
Navigating this compliance maze might seem daunting, but there are solutions. If your healthcare app requires adherence to HIPAA, a first step could be to implement proven HIPAA best practices such as PHI data stripping through data anonymization.
For instance, services like Amazon Comprehend Medical can detect and assess PHI entities in the clinical text according to HIPAA’s guidelines, such as names, ages, and addresses. With confidence scores to gauge the accuracy of detected entities, you can easily filter this information according to a threshold suitable for your application.
While PHI data is filtered during processing, it can be reintegrated again into the final response as needed. This preserves essential information without exposing sensitive PHI to external endpoints like OpenAI. In doing so, we maintain data integrity and alignment with HIPAA’s strict privacy and security standards.
In essence, this approach ensures that patient data:
- Is never exposed to external sources
- Remains securely encrypted within a provider’s cloud environment
Entering into a BAA agreement
If that does not meet your needs, consider forming a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with vendors like OpenAI. A BAA is a contract that defines both your and the vendor’s obligations in maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of protected health information (PHI). Though you remain accountable for overall PHI protection, the vendor assists in processing or managing PHI in line with regulations. The agreement outlines the allowed uses of PHI, the necessary safeguards, and the process for reporting breaches. By executing a BAA, you foster a formal partnership to manage sensitive data, ensuring technological and legal alignment with HIPAA.
Self-hosted language models
Hosting a ChatGPT model on your own servers is another viable route that allows greater control over patient health information (PHI) security and customization to meet HIPAA compliance requirements. This method ensures PHI never reaches third-party servers, minimizing data breach risks but also bringing considerable complexity. Training, maintaining, and fine-tuning a self-hosted large language model (LLM) require substantial resources and technical expertise.
Fine-tuning refers explicitly to adjusting an existing model to handle specific tasks more effectively, often with domain-specific information. This customization offers the potential for more accurate responses but comes with challenges, including costs for extensive data collection and computation.
A notable risk in this process is the occurrence of hallucinations, where LLMs may generate false or offensive content, necessitating vigilant control measures. Meticulous planning for security measures such as encryption, regular audits, and extensive testing are also crucial, making the process potentially costly and intricate.
Read more on Large Language Models in Healthcare in our blog.
Utilizing Out-of-the-Box Solutions and Secure APIs
When building chatbots powered by generative AI, leveraging out-of-the-box solutions and secure APIs can significantly streamline the process. These tools provide robust mechanisms to handle sensitive patient data securely.
- Out-of-the-Box Solutions: Platforms like BastionGPT and CompliantGPT offer automated PHI de-identification services that ensure compliance seamlessly. These solutions automatically strip out PHI before processing and reinsert it after, maintaining data privacy.
- Secure APIs: Utilize HIPAA-compliant APIs such as Amazon Comprehend Medical, Azure OpenAI, or Google Cloud Healthcare API to manage sensitive data. These APIs are designed to handle PHI securely, providing essential features like encryption and access controls.
By integrating these tools into your workflow, you can expedite app development and efficiently handle PHI while adhering to HIPAA regulations.
Implementing Traditional HIPAA Safeguards
In addition to specialized tools, traditional HIPAA safeguards remain crucial in ensuring the security and privacy of patient data. These measures are foundational to any compliant system:
- Data Encryption: Ensure end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit to protect against unauthorized access.
- Adhere to SOC-2 Principles: Follow SOC-2 guidelines to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards that protect sensitive information.
- Multi-factor Authentication: Utilize multi-factor authentication to enhance security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access.
- Role-Based Access: Implement role-based access controls to limit data access to authorized personnel only, thereby reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Audit Logging: Maintain detailed logs of data access and modifications to enable accountability and traceability.
- Remove PHI from Push Notifications: Ensure that push notifications do not contain any PHI to prevent accidental exposure.
By adhering to these established practices, you reinforce the security framework of your AI-enabled chatbot, ensuring it meets HIPAA standards comprehensively. These combined measures create a robust defense against potential breaches and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of patient data, which is paramount in any healthcare setting.
Addressing Bot Hallucinations
In AI and medical chatbots, hallucinations refer to instances where an AI model may generate misleading or nonsensical information that fails to correspond to actual facts. These hallucinations can range from minor grammatical mistakes to significant textual inaccuracies.
In medical chatbots, this could translate into incorrect medical advice or baseless health claims—a concern that must be carefully managed and mitigated.
Also Read: Mental Health Chatbot Development
Why do hallucinations occur?
Medical chatbots operate on a complex yet fascinating principle. Think of them as text predictors, predicting the next word in a sentence, much like filling in a blank in a statement. For instance, given the phrase “I went,” the chatbot evaluates what might logically follow, such as “home” or “eating.”
These chatbots generate coherent responses by continuously predicting the next word based on internalized concepts. The AI systems that power these chatbots are generally trained on large amounts of data, often in terabytes, enabling them to generate replies across various topics.
 This process occasionally results in inconsistencies or incorrect information for several reasons. A chatbot might lack the precise information in its training data to answer a question and consequently fabricate a response. It may also draw from fictional or subjective content in its training data, leading to potentially misleading answers.
This process occasionally results in inconsistencies or incorrect information for several reasons. A chatbot might lack the precise information in its training data to answer a question and consequently fabricate a response. It may also draw from fictional or subjective content in its training data, leading to potentially misleading answers.
Another contributing factor is the chatbot’s inability to admit a lack of knowledge, leading it to generate the most probable response, even if incorrect. Recognizing these underlying complexities helps developers and users align chatbots with real-world applications more responsibly.
Consequences of hallucinations
In the world of medical chatbots, the consequences of hallucinations can be significant and severe:
- Misinformation: Providing incorrect health information can lead to misunderstandings and incorrect self-diagnosis, resulting in potential panic or complacency about a medical condition. Chatbots that provide false information on appointments, insurance coverage, billing, or medical records can lead to missed appointments, financial misunderstandings, or inaccuracies in personal health records.
- Legal Implications: Non-compliance with medical guidelines or regulations due to hallucinations may expose developers and healthcare providers to legal risks, such as fines, penalties, or lawsuits. These legal actions can result in significant financial burdens, reputational damage, and potential loss of licensure or certification for those involved.
- Loss of Trust: Frequent hallucinations may erode users’ trust in the technology, hampering its adoption and effectiveness in healthcare settings.
If confidence is significantly diminished, patients may avoid using chatbots altogether, missing out on potential benefits and advancements in healthcare delivery and communication.
Mitigating Hallucinations in Medical Chatbots
Below we explore key strategies for managing bot hallucinations and ensuring reliable information delivery:
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Leveraging verified data sources to ground responses.
- Advanced Prompt Engineering: Techniques like explicit instructions and multi-step reasoning to guide GPT towards accurate outputs.
- Automated Hallucination Detection: Utilizing tools to identify and flag potentially fabricated content.
We’ll delve deeper into each approach in the following sections, outlining their benefits and best practices for implementation.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Addressing hallucinations in medical chatbots calls for strategies that reduce the risk of incorrect or misleading information. One practical approach is to use external databases with augmented knowledge, where the information has been thoroughly vetted by medical experts.
What is RAG?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) can be a powerful tool for enhancing your ChatGPT-based medical chatbot. RAG combines the strengths of two approaches:
- Retrieval: A separate model searches a curated database of medical records, patient preferences documents, and relevant guidelines for senior care. This database could include information like: past medical history, allergies, medications, cognitive and functional limitations.
- Generation: ChatGPT, or a similar LLM, then takes the retrieved information and uses it to generate a comprehensive response tailored to the medical assistant’s query.
Of course, we need to be mindful of data security and curation when adopting the RAG approach. The database used by the RAG system must be secure and compliant with HIPAA regulations. And the quality and accuracy of the data in the database will directly impact the chatbot’s performance.
Benefits for your Medical Chatbot
- RAG ensures the chatbot provides accurate and specific information about patients based on their actual medical records and preferences.
- Medical assistants and provider won’t have to sift through vast amounts of data to find the information they need.
- Faster access to accurate information can lead to better decision-making and improved patient care.
How Does RAG Work aka How Do I Get Accurate Patient Data?
Here’s how this approach of smart application of generative AI in medical chatbots works, step-by-step:
- User Interaction: A user initiates a conversation by asking questions in the chatbot interface.
- NLP Application: The chatbot employs NLP semantic search techniques to locate the most pertinent information within a pre-verified database. Semantic search is a method that comprehends the context and intent of a user’s query, enabling it to find information specifically tailored to that request. This approach is analogous to searching for information on Google, providing contextually relevant results beyond mere keyword matching.
- Information Retrieval: Based on the top results, the necessary information is pulled into the GPT prompt, providing the context for a precise response.
- Contextualized Response: GPT synthesizes the pulled information and user query to provide an answer grounded in verified data, minimizing the risk of generating incorrect or misleading content.
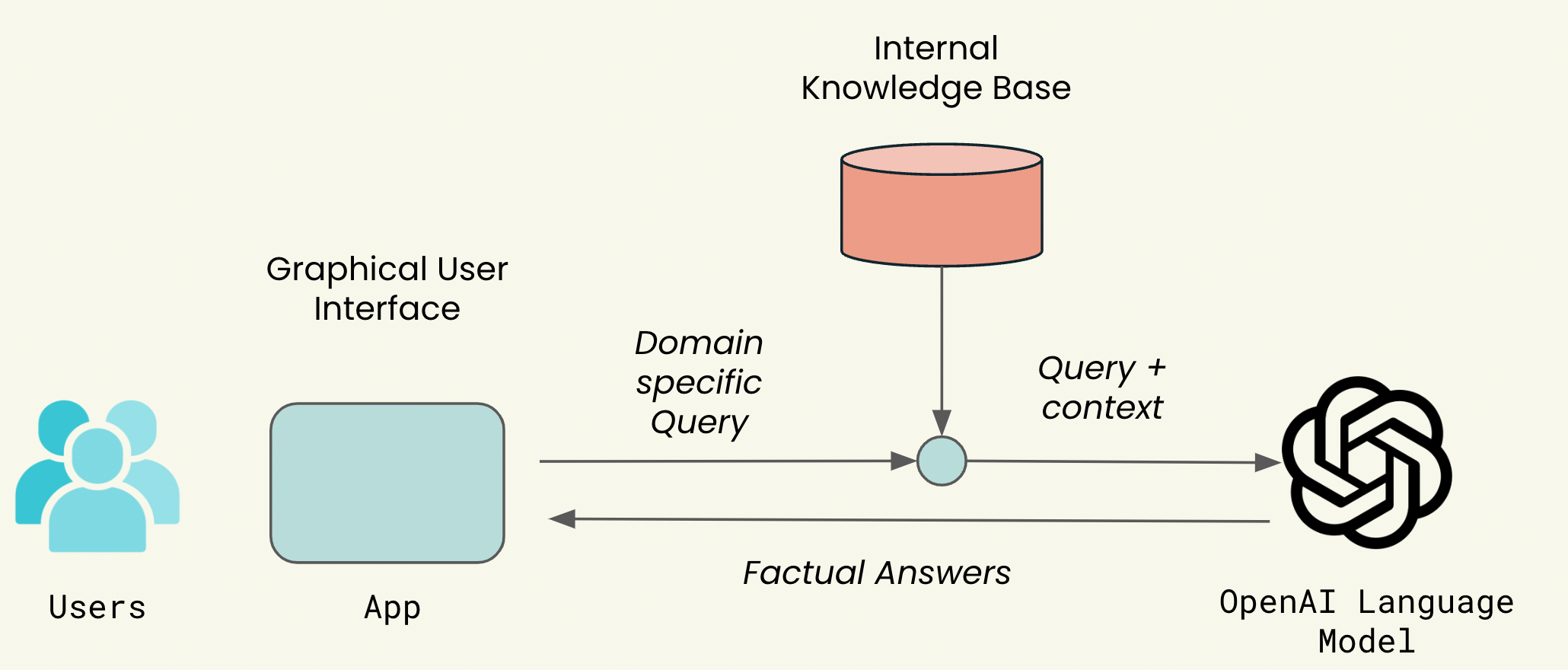
Pulling verified information into the chatbot system enables the bot to answer questions based on credible and accurate data rather than generating an answer from scratch.
This provides the chatbot with contextual information to craft appropriate responses and acts as a safeguard against the generation of erroneous or fabricated content.
Best Practice for Working with RAG
Successfully implementing Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) in medical chatbots is a pretty straightforward technique for expert AI healthcare developers. However, you might need to keep in mind a few things to get the best out of the generative AI tech in your health chatbot:
- Vector Database Conversion and Storage: Documents need to be converted and stored in a vector database, which facilitates easy lookup. This process ensures that relevant information can be quickly accessed based on user queries.
- Utilizing Automated Solutions to Bootstrap Development: Platform like BastionGPT or Microsoft Azure OpenAI allows referencing documents directly, handling the conversion and storage process automatically. Vector database services like Pinecone or Weaviate can also be considered for robust document handling.
- Meta-Data Tagging: Consider tagging metadata information within the vector database to correctly identify patients and enhance the accuracy of retrieved information.
- Data Validation Mechanisms: If we pull PHI directly from Electronic Health Records (EHR) to ensure data accuracy, the data remains reliable and accurate. However, if we need to update an EHR through a GPT-powered app using two-way sync, we must implement some validation mechanisms for new data inputs before syncing back to the EHR. Use verification checks or human review processes to confirm data integrity.
By implementing these best practices, you can optimize your RAG system to provide accurate and reliable information, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of your medical chatbot.
Addressing Bot Hallucinations with Advanced Prompt Engineering
Another effective strategy is leveraging advanced prompt engineering techniques to enhance the accuracy and relevance of the medical chatbot’s output. Here are a few prompt engineering techniques to apply:
Explicit Instructions
In the system prompt, explicitly instruct the model to provide answers solely based on the given context. If the context is insufficient, the model should respond with “Not Enough Information”.
Step-by-Step Reasoning: Chained GPT Calls
Encourage the model to reason out the answer step-by-step before providing the final output. This deliberate approach can help ensure the response is well-considered and accurate. Implement multiple GPT calls at each step of the response generation process. This method allows the model to be more meticulous when generating and evaluating outputs.
Initial Retrieval Evaluation
After retrieving initial information, use GPT to determine if parts of the retrieved text are relevant to the user query. The model should exclude irrelevant text if it is not relevant. Make an additional GPT call to ask if the final answer is justified based on the current context. The model should redraft the answer if the answer is not justified.
Automated Hallucination Detection
Utilize APIs that automatically evaluate whether a given output is prone to hallucinations. Tools like Vectara Factual Consistency Score and Hugging Face’s hallucination evaluation model can help in this automated assessment process.
These techniques aim to make GPT “think” more deliberately about its responses, significantly reducing the risk of hallucinations and enhancing the chatbot’s reliability.
Addressing hallucinations and ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA is paramount in the development of medical chatbots. But what are the tools that can assist in this endeavor?
Platform Recommendations
It is essential to consider chatbot development platforms that facilitate not only robust interaction but also ensure that the data handling is in line with the highest security standards.
Vectara
In terms of specific recommendations, Vectara stands out as a solid option. Specializing in semantic search, their platform enables ChatGPT-like conversations within the context of your particular data.
They offer features that simplify the complex process of data handling. For example, users can upload data via drag-and-drop functionality or use APIs to input information directly into their database. This effectively streamlines the first three steps in the process, reducing chatbot development costs and enabling a quicker launch of the initial iteration of the chatbot.
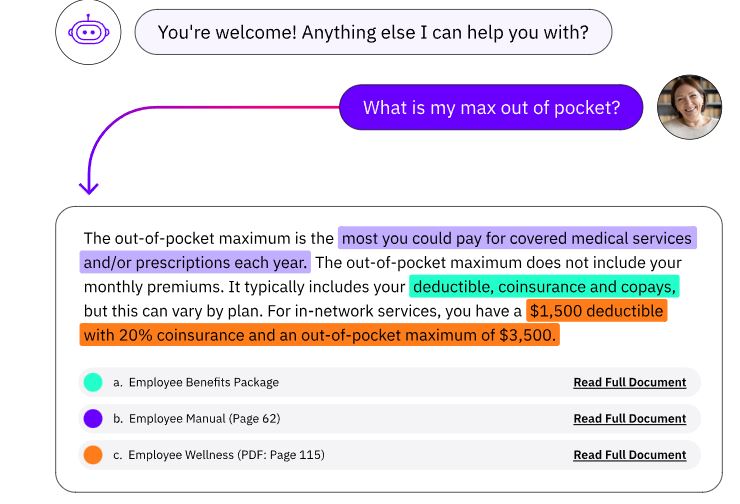 Vectara’s platform offers valuable services such as the “Summary API,” which generates concise responses based on user queries, and the “Search API,” which displays the raw top search results for further examination.
Vectara’s platform offers valuable services such as the “Summary API,” which generates concise responses based on user queries, and the “Search API,” which displays the raw top search results for further examination.
As an API-first platform, users can use the outputs of either and tailor them using another model like OpenAI’s GPT, ensuring context-appropriate responses.
The Summary API can generate standard responses or be customized; however, adding extra models for customization may impact the chatbot’s responsiveness. What sets Vectara apart is its unwavering commitment to security. Their cloud service provider AWS is known for complying with numerous security standards, including HIPAA.
Vectara also employs advanced measures to safeguard user information. This includes protecting data during transmission and storage and implementing robust procedures to monitor and review the system for potential misuse. Such a comprehensive approach streamlines the development of efficient medical chatbots and reinforces trust in the system’s integrity and security.
Scale
In addition to Vectara, Scale is another excellent option to consider. Their platform is a beacon of efficiency, allowing teams to deploy production-ready GPT applications in just minutes.
Related: Using ChatGPT in Healthcare
With several models to choose from, easy-to-deploy endpoints, and a straightforward setup for databases to store information, Scale offers a comprehensive solution.
Their commitment to HIPAA compliance is indicative of a determined effort to safeguard sensitive patient health information (PHI), making Scale a secure and compliant data platform for AI medical chatbots.
Also Read: Healthcare App Development Guide
In both Vectara and Scale’s offerings, the pay-as-you-go model offers a significant advantage, providing flexibility and reducing costs in developing medical chatbots.

Proper Redirection to Human Operators
One of the critical elements in creating a successful medical chatbot is the ability to direct interactions to human assistants when needed. This feature is essential for handling highly specialized or emotional situations and scenarios where the chatbot lacks meaningful context to answer a query.
When faced with a question outside its understanding, a medical bot should admit its limitations and defer to human expertise. This redirection isn’t merely a technological feature; it signifies a steadfast commitment to patient-centered care and safety.
A simple way to redirect appropriately is by using OpenAI’s system prompt. The system prompt comprises an initial set of instructions defining the chatbot conversation’s boundaries. It establishes the rules the assistant must adhere to, topics to avoid, the formatting of responses, and more.
We can explicitly guide the chatbot’s behavior using the system prompt, ensuring it aligns with the desired patient-centered care and safety standards. Here is an example illustrating this concept:
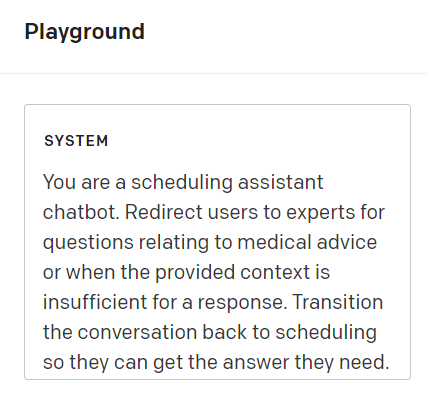
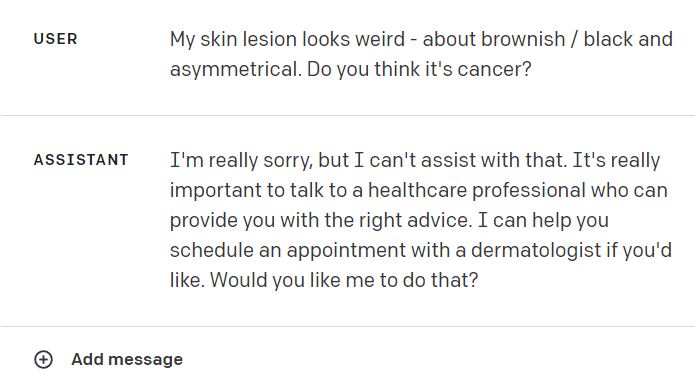 If we design a scheduling chatbot, users might inquire about medical advice for their specific conditions (like cancerous lesions in our example above). The system prompt can be set up to redirect these queries, ensuring the bot refrains from giving medical advice and instead schedules them with the relevant experts for a proper response.
If we design a scheduling chatbot, users might inquire about medical advice for their specific conditions (like cancerous lesions in our example above). The system prompt can be set up to redirect these queries, ensuring the bot refrains from giving medical advice and instead schedules them with the relevant experts for a proper response.
We can apply a similar approach if the chatbot lacks the context to answer the question even after applying semantic search.
Top Medical Chatbots
As the medical world embraces AI, several chatbots have risen to the forefront due to their exceptional features, patient engagement, and accurate information dissemination. Here are some of the leaders in this arena:
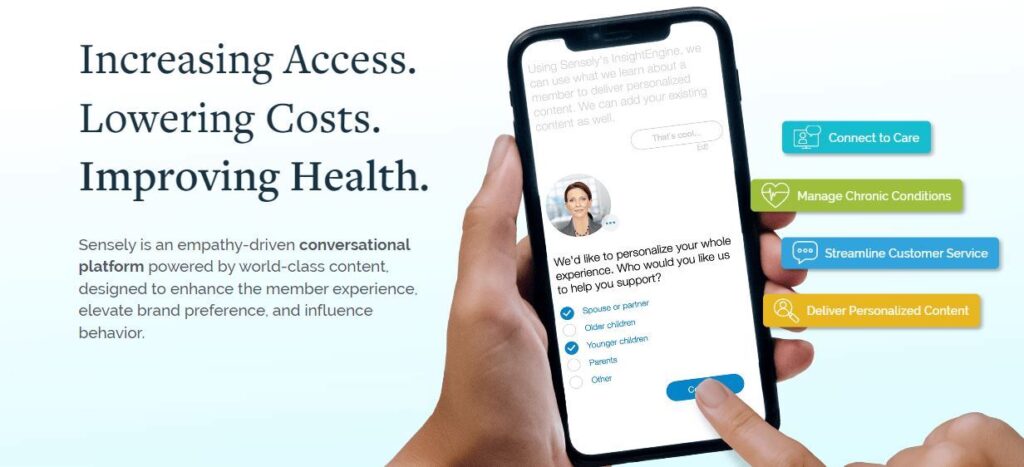
Sensely
Sensely is revolutionizing patient engagement with its AI-driven avatar. This chatbot employs a multi-sensory approach, blending voice and visuals to interact with patients, making the experience more human-like.
Primarily designed to aid patients with chronic conditions, Sensely offers medication reminders, symptom checkers, and general health information. Health management stands as one of Sensely’s core features. Users can tap into trusted healthcare content from esteemed sources like the Mayo Clinic and NHS, ensuring they’re equipped with reliable information.
Image credit: Sensely (all image rights belong to Sensely Inc)
Florence
As the world’s premier online symptom checker, Florence is celebrated for its straightforward design and commitment to dispelling health misinformation.
Since the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, it has played a crucial role in providing accurate virus-related information. Users simply input their symptoms, and Florence promptly suggests potential causes and recommended actions.
Through its interactive queries, Florence offers symptom assessment and advice on stress management, proper nutrition, physical activity, and quitting tobacco and e-cigarettes.
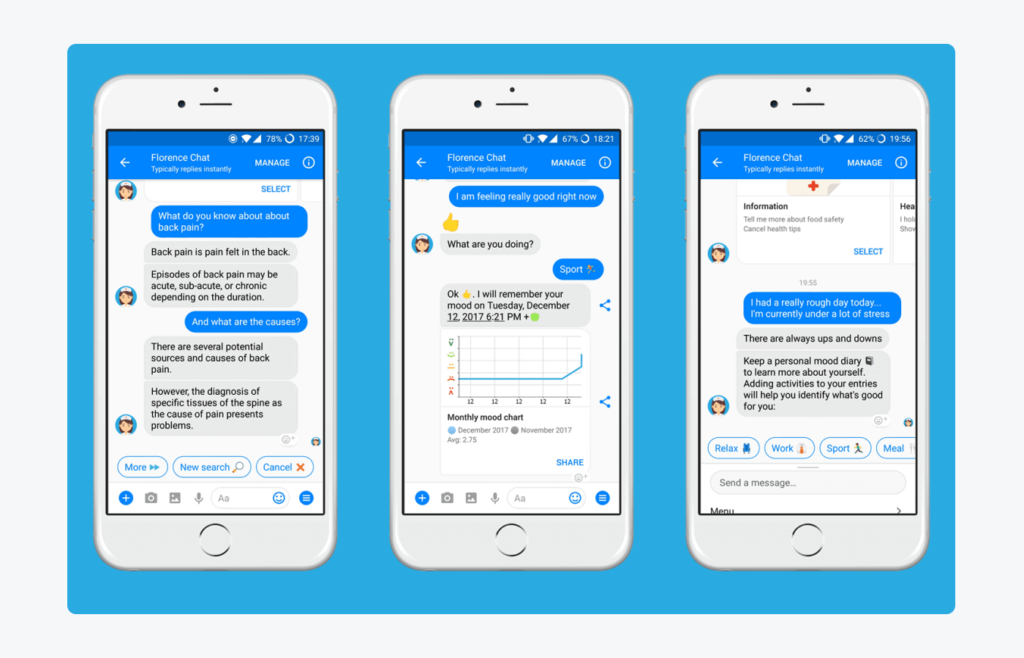
Image credit: PACT Care BV (all image rights belong to PACT Care BV )
Additionally, the bot aids in medication reminders, body metric tracking, and finding nearby health professionals. Its comprehensive features, combined with an intuitive interface, have made Florence a top choice for many.
Buoy Health
Taking a step beyond traditional symptom checking, Buoy Health employs advanced AI algorithms to conduct a back-and-forth conversation with users, mirroring a real doctor-patient interaction.
Buoy offers a more tailored assessment of potential health issues by understanding the context and diving deep into the symptoms. Buoy Health sets itself apart through its interactive AI approach and prioritizes delivering accurate and up-to-date health information.
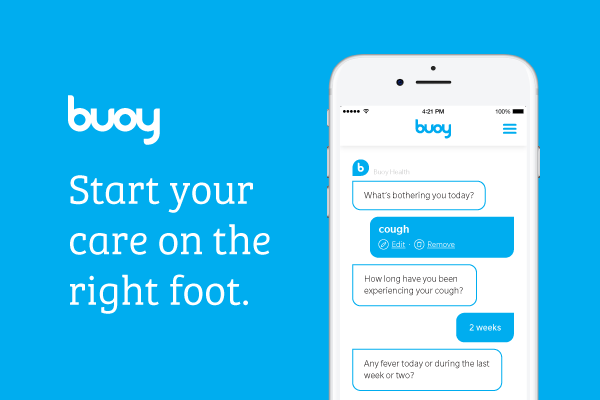
Image credit: Buoy Chatbot (all image rights belong to Buoy Health, Inc.)
Recognizing the importance of trustworthy sources, Buoy partners with or references esteemed institutions like the Mayo Clinic and Harvard Medical School, ensuring users receive advice grounded in well-respected medical expertise.
Babylon Health
Pioneering the future of telemedicine, Babylon Health is not just a chatbot but a comprehensive digital health service platform. At its core, Babylon employs a sophisticated AI-driven chatbot that assists users in understanding their symptoms and navigating potential medical concerns.
Beyond its symptom checker capabilities, Babylon provides video consultations with real doctors, giving patients direct access to medical professionals from the comfort of their homes.
In recent years, Babylon Health has expanded its reach and now offers digital health services in several countries worldwide. A standout feature of Babylon is its Healthcheck tool, which provides users with a personalized health report and lifestyle advice, paving the way for proactive health management.

Why Topflight Nails Medical-Chatbot Builds
Need a HIPAA-safe chatbot that actually answers clinical questions instead of hallucinating? That’s exactly what we delivered with Mi-Life. Caregivers at Goldie Floberg had to wade through 1,300 pages of policies; in ~1,100 engineering hours we gave them a voice- and text-driven bot that retrieves patient-specific data in seconds, thanks to a retrieval-augmented-generation (RAG) pipeline backed by a vector database. The result: fewer medication errors and a sky-high staff NPS, all while keeping PHI locked down behind OTP log-ins and automated de-identification.
That playbook—GenAI strategy, full-cycle dev, and bullet-proof compliance—is the same one front-and-center on our homepage, where we position ourselves as the AI + healthcare development partner.
Why founders choose Topflight for medical chatbots
Hallucination-proof answers – RAG pipelines, metadata tagging, and defensive “I don’t know” responses keep the bot honest.
Voice & text UX out-of-the-box – Hands-free queries built in React Native let clinicians grab data while juggling real patients.
HIPAA by default – PHI de-identification, role-based access, and Azure OpenAI hosting mean security reviews become paperwork, not panic.
MVPs in weeks, not quarters – Cross-platform stacks and reusable GenAI modules deliver live pilots while competitors are still scoping.
Ready to Build Your Medical Chatbot?
After thoroughly delving into the complexities of HIPAA compliance, tackling the issue of addressing hallucinations in medical chatbots, and exploring various platforms and solutions, it becomes clear that creating a successful medical chatbot is a multifaceted undertaking.
Also Read: How to Make a Chatbot from scratch
As renowned app developers with significant expertise in generative AI, we offer a unique blend of technical expertise and a keen understanding of the healthcare domain.
One of our standout projects, GaleAI, showcases how we successfully implemented generative AI while strictly adhering to HIPAA guidelines and ensuring proper data handling. This innovative solution transforms medical notes into accurate medical codes in mere seconds.
Whether you’re keen on exploring Vectara, Scale, OpenAI, or any other cutting-edge platform or seeking guidance on mitigating risks like hallucinations, we’re here to assist.
Contact us if you need a personalized consultation or are contemplating integrating AI-driven enhancements to your medical chatbot. Let’s co-create solutions that prioritize both innovation and patient care.
[This blog was originally published on 8/16/2023 and has been updated with more recent content]
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of a system prompt in a medical chatbot?
The system prompt ensures the medical chatbot’s behavior aligns with patient-centered care and safety standards. For instance, when users inquire about medical advice, the system prompt can redirect these queries to schedule them with the relevant experts, preventing the chatbot from giving medical advice.
What are the potential consequences of hallucinations in medical chatbots?
One effective strategy to mitigate hallucinations in medical chatbots is to use external databases with augmented knowledge, where the information has been thoroughly vetted by medical experts. Integrating this verified information into the chatbot system enables the bot to answer questions based on credible and accurate data, reducing the risk of erroneous or fabricated content.
What are the potential consequences of hallucinations in medical chatbots?
The consequences of hallucinations in medical chatbots can be severe, including misinformation in health advice that may lead to misunderstandings or incorrect self-diagnosis. This misinformation can extend to scheduling appointments, insurance coverage, billing, or medical records, leading to significant complications. There are also legal implications, such as non-compliance with medical guidelines or regulations, which can result in fines, penalties, or lawsuits. Frequent hallucinations can erode users’ trust in the technology, potentially reducing its adoption and effectiveness in healthcare settings.
What is the relevance of HIPAA in medical chatbot development?
HIPAA, or the Health Insurance and Portability and Accountability Act, sets the regulatory standards for managing, using, and storing sensitive healthcare information. Any AI assistant handling protected health information (PHI) must comply with HIPAA, making it a critical consideration in medical chatbot development.
What strategies can be employed to navigate HIPAA compliance in medical chatbot development?
Developers can utilize services like Amazon Comprehend Medical for PHI data stripping through data anonymization. Moreover, forming a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) with vendors like OpenAI helps manage PHI in line with regulations. Additionally, self-hosting a ChatGPT model enables more control over PHI security.