ChatGPT in healthcare is all the craze in today’s medical world. And while some keep arguing about AI being unable to replace human healthcare providers, thoughtful observers note more and more compelling use cases for applying the novel technology in medicine.
In fact, ChatGPT developed by OpenAI has already proven its efficiency, even without additional training by healthcare professionals. The most recent AI chatbot’s accomplishments include:
- passing the United States Medical Licensing Exam (minus the questions requiring visual assessment)
- outperforming human physicians in the quality and empathy of responses
- identifying new compounds that could be used to treat COVID-19
While healthcare ChatGPT use cases continue to wow the public, let’s discuss how providers can use this large language model (LLM) technology in their medical practices today, ushering in a new era of virtual health.
Top Takeaways:
- The success of a ChatGPT-based healthcare solution will largely depend on moated, proprietary data and research blended with a comprehensive user experience, which is hard to achieve with prompt engineering alone.
- ChatGPT use cases in healthcare are limited to natural language processing (NLP) scenarios for the time being. At the same time, consumer interfaces don’t have to be tied to text 100%: speech-to-text and text-to-speech are also viable options. As this tech matures, the intersection of ChatGPT and healthcare use cases will reveal a thrilling panorama of possibilities.
- Applying large language models like ChatGPT in the medical field poses a serious challenge from the development perspective. Successful project completion requires considerable refurbishment of DevOps, QA testing, and other AI/ML development disciplines.
Table of Contents:
- Top 17 Use Cases of ChatGPT in Healthcare
- Benefits of Using ChatGPT in Healthcare Applications
- Recommendations for Using ChatGPT in Healthcare
- Challenges of Developing a ChatGPT-Powered Health App
- HIPAA Compliance Concerns
- What’s Next for ChatGPT in Healthcare?
- Topflight’s Experience with ChatGPT in Healthcare Apps
Top 17 Use Cases of ChatGPT in Healthcare
ChatGPT has the potential to transform the healthcare industry by improving patient outcomes, reducing costs, and increasing efficiency.
Its natural language processing capabilities allow it to communicate with patients in a way that is both comfortable and effective, and its ability to quickly analyze vast amounts of data can provide healthcare providers with valuable insights. How will ChatGPT affect healthcare?
At a bird’s eye view, we’re looking at these three immediately practical areas for ChatGPT application in medical software:
- conversational interfaces
Think patient- and provider-facing chatbots and/or human-like virtual assistants.
- information retrieval from large datasets
Think running an auto-generated report based on patient data that meets specific criteria to provide information to doctors.
- automated content generation
Think lab results sent to patients where they can ask for an explanation from a bot.
Considering the vast potential and emerging trends in medical innovation, these three directions are exactly how providers may use ChatGPT in healthcare to revolutionize patient care, streamline processes, and make significant strides in medical research.
Large language models like ChatGPT effectively replace patient-provider interactions when human intervention is optional. As a result, patients can learn about their conditions and treatment plans or interpret test results at their own pace. At the same time, providers can tap into this NLP technology to process massive amounts of various health data and gain insights faster or create documentation in a snap. Thus, the use of ChatGPT in healthcare continues to redefine patient and provider experiences.
Here are the most promising use cases for applying Chat GPT in healthcare settings:
- Disease diagnosis
- Predicting medical outcomes
- Personalized medicine
- Patient education
- Mental health support
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
- Drug discovery
- Clinical trial matching
- Patient triage & conversational symptom checking
- Medical coding automation
- Claims denial management & appeals
- Prior authorization support
- Quality reporting & compliance automation
- Electronic health record (EHR) management
- Voice-to-note automation (ambient scribing)
- Chatbot assistants for healthcare providers
- Medical education
Now, let’s review each use case one by one.
Read more on chatbots in healthcare in our blog.
#1. Disease diagnosis
ChatGPT can assist healthcare providers in diagnosing diseases. It has been trained on large datasets of medical literature and electronic health records, enabling it to understand medical terminology and symptoms. ChatGPT can analyze patient symptoms and medical history to suggest possible diagnoses to healthcare providers. This potent combination of Chat GPT and healthcare can lead to swifter and more precise medical diagnosis, thereby enhancing patient outcomes by offering timely and accurate treatment solutions.
#2. Predicting medical outcomes
Chat GPT in medicine has the ability to not only diagnose diseases but also predict medical outcomes and potential side effects. A recent study has shown that ChatGPT can predict patient outcomes (by analyzing health status), such as length of hospital stay, readmission, and mortality, more accurately than human physicians. This has significant implications for improving patient care and reducing healthcare costs.
Related: Chatbot Development Costs

#3. Personalized medicine
Chatbots can also assist in the development of personalized medicine. By analyzing patient data, medical notes, and medical history, ChatGPT can provide insights into the best treatment options for individual patients. This can help providers tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique needs and increase the effectiveness of treatments.
Exploring Chat GPT for healthcare use cases reveals a new dimension of personalized care, where treatment is not just reactive but proactive and tailored to an individual’s unique needs.
#4. Patient education
ChatGPT can assist patients in understanding their medical conditions and treatment options. It can provide personalized education on medical conditions, medication use, and healthy lifestyle choices. This can improve patient adherence to personalized treatment plans and lead to better health outcomes.
Implementing a ChatGPT for medical use could potentially revolutionize patient education by providing customized and accessible information at the touch of a button. This ‘medical version’ of ChatGPT could prove invaluable in enhancing patient understanding and adherence to treatment plans, ultimately driving better health outcomes.
#5. Mental health support
Mental health is an area that could benefit greatly from the use of chatbots powered by ChatGPT. Patients who are struggling with mental health issues may feel hesitant to seek help or may not have access to mental health services. A chatbot can provide an accessible and confidential way for patients to get the help they need.

ChatGPT can analyze patient responses to mental health screening tools and provide personalized support and resources, such as self-care tips and coping mechanisms. This can lead to improved mental health outcomes for patients.
Related: Mental Health App Development Guide
The use of healthcare GPT in mental health support shows promising potential to transform the way patients receive help and guidance. Further, the ability of these AI-powered chatbots to provide customer support around the clock ensures that individuals have access to immediate assistance, reducing the barriers to seeking help and potentially improving mental health outcomes.
Also Read: Build Mental Health Chatbot
Additionally, chatbots can monitor patients for signs of mental health issues and provide early intervention when necessary.
#6. Remote patient monitoring (RPM)
Healthcare Chat GPT solutions can be used to remotely monitor patients’ health. It can analyze patient data, such as blood pressure and heart rate, and alert healthcare providers to any abnormalities. This can lead to earlier intervention and better patient outcomes.
Related: A Guide to RPM Development
Providers can use the chatbot to check in on patients after surgery or to remind them to take their medication. The chatbot can also provide a way for patients to communicate with their providers in a non-intrusive way by asking a question or reporting a symptom.
And have you ever thought about the synergy between Chat GPT and medicine in terms of enhancing provider-patient communication? Patients get a convenient and non-intrusive avenue to communicate with their healthcare providers. They can ask questions or report symptoms at any time, making it an ideal solution for remote patient monitoring. Moreover, the data gathered can aid in clinical decision support, enabling healthcare providers to make well-informed judgments about patient care.
Also Read: Unleashing the power of Generative AI in healthcare
#7. Drug discovery
ChatGPT can also be used in drug discovery and development. Developing new drugs is a time-consuming and expensive process, and the use of chatbots powered by ChatGPT can help streamline the process. Chatbots can assist researchers in identifying potential drug targets and predicting new drug efficacy.
A ChatGPT-enabled healthcare app can assist in drug discovery by analyzing large datasets of chemical compounds and identifying potential drug candidates. This can lead to faster and more efficient drug discovery processes.
#8. Clinical trial matching
When it comes to clinical trials, ChatGPT is an exceptional tool that can provide healthcare organizations with a great deal of support in terms of analyzing patient data and finding the right candidates for a trial. This method can significantly accelerate the process of patient enrollment in clinical trials, ultimately leading to quicker drug approvals.
So, when a provider is looking to streamline their clinical trial process, AI ChatGPT in healthcare is definitely worth considering.
Read more on clinical trial software development
#9. Patient triage & conversational symptom checking
While traditional symptom checkers rely on rigid logic trees, ChatGPT brings nuance to patient triage by analyzing free-form input and delivering dynamic, context-aware responses. Patients can describe symptoms in their own words, and ChatGPT responds with follow-up questions, severity assessments, and potential next steps — like scheduling care or recommending home treatment.
This makes Chat GPT for medical professionals a valuable frontline tool for triage, especially in telehealth environments or remote areas where in-person consultations are limited. It improves patient satisfaction, optimizes visits, and integrates seamlessly with digital front doors and wearable-linked portals.
#10. Medical coding automation
Medical coding is one of the most time-consuming and error-prone tasks in healthcare administration. ChatGPT can be fine-tuned to understand clinical documentation and translate it into accurate billing codes such as ICD-10, CPT, or SNOMED. Instead of relying solely on human coders, organizations can leverage ChatGPT to auto-suggest codes based on free-text clinical notes, flag inconsistencies, and even pre-fill claim forms. This not only accelerates the revenue cycle but also reduces costly denials and resubmissions. AI-powered medical coding also supports value-based care by capturing the right clinical complexity upfront.
#11. Claims denial management & appeals
Claims denials create major financial bottlenecks for healthcare organizations. ChatGPT can analyze payer denial letters, identify root causes, and suggest appropriate corrective actions. More impressively, it can draft detailed appeal letters or justification statements, pulling supporting documentation directly from patient records. This reduces the manual work required by billing teams and shortens revenue cycles. For provider groups facing mounting pressure from payers, using ChatGPT for denial management can be a game-changer in increasing recovery rates.
#12. Prior authorization support
Navigating payer policies for prior authorizations is notoriously complex. ChatGPT can simplify this process by analyzing patient records and cross-referencing them with insurer documentation requirements. It can highlight which clinical criteria have been met, suggest which documents to submit, and even draft structured authorization requests.
By proactively identifying gaps before submission, ChatGPT helps avoid costly treatment delays and denial appeals. This use case is especially valuable in high-volume specialties like radiology, cardiology, and orthopedics where pre-auths are the norm.
#13. Quality reporting & compliance automation
Quality reporting for programs like MIPS, ACO, or HEDIS often drains resources from clinical teams. ChatGPT can streamline this by extracting reportable data from EHRs, aligning it with regulatory requirements, and generating documentation summaries or metric narratives.

For example, it can flag patients missing key screenings or summarize encounters to justify quality metrics. This ensures that compliance deadlines are met while minimizing the burden on providers and staff. It’s a quiet but high-impact use case, especially for large provider groups or risk-bearing entities.
#14. Electronic health record (EHR) management
ChatGPT can assist in EHR management by analyzing patient data and identifying potential errors or inconsistencies. This can lead to improved data quality and more accurate diagnoses and treatment recommendations.
For example, a recent collaboration between Microsoft and Epic Systems aims to improve electronic health record (EHR) management using ChatGPT-4. The plan is to develop an EHR search engine to quickly retrieve relevant information from patient medical records and flag potential issues.
Related: A Complete Guide to EHR/EMR Integration
This technology can potentially be a game-changer for healthcare providers who struggle with the time-consuming and often frustrating task of manually sifting through EHR data.
#15. Voice-to-note automation (ambient scribing)
Ambient clinical documentation is rapidly becoming one of the most powerful use cases for ChatGPT. By listening to patient-provider conversations, ChatGPT can generate structured SOAP notes in real time or post-visit — saving providers hours each week. Unlike standard transcription tools, this approach captures clinical intent, highlights relevant diagnoses, and adds summaries in natural language.
It also adapts to specialty-specific workflows (e.g., primary care vs. dermatology). Many EHR vendors are actively piloting these AI-powered scribes, positioning them as the next step in clinician productivity.
#16. Chatbot assistants for healthcare providers
Medical ChatGPT can assist healthcare providers in their day-to-day operations. For instance, a physician can ask the chatbot for a quick medical summary of a patient to get an overview of the patient’s medical history, which can be time-consuming and often requires sifting through medical records. ChatGPT can also help providers stay updated with the latest medical knowledge and research by providing relevant articles and studies on countless health topics.
Furthermore, the use of ChatGPT for medical research has proven to be a game-changer, as it can swiftly sift through volumes of medical documentation and provide physicians with the most recent and relevant medical findings, enhancing their knowledge base and informing treatment plans.
#17. Medical education
As a language model trained on a vast corpus of text, ChatGPT can be a valuable resource for medical education. It can assist in various ways, such as providing quick and accurate answers to medical queries, generating summaries of complex medical concepts, and helping students with their research.
Read more on how to use AI to summarize medical records
ChatGPT can also provide access to a vast amount of medical literature and research papers, making it an excellent tool for students and medical professionals looking to stay up-to-date on the latest developments in their field.

Furthermore, ChatGPT can help in creating medical content, such as educational videos, tutorials, and online courses, making medical education more accessible to people around the world.
Benefits of Using ChatGPT in Healthcare Applications
As ChatGPT finds its way into everything from virtual assistants to back-office automation, its impact goes beyond isolated use cases. At a system-wide level, ChatGPT delivers transformative benefits that cut across departments, workflows, and patient touchpoints.
Below are the most significant advantages healthcare organizations can unlock by integrating ChatGPT into their digital infrastructure:
- Improved operational efficiency
- Faster clinical decision-making
- Reduced documentation burden
- Increased patient engagement and satisfaction
- Cost savings across care delivery
- Enhanced scalability of care teams
- 24/7 availability without burnout
- Accelerated innovation and research
- More equitable access to information
Improved operational efficiency
One of the most immediate ChatGPT applications in healthcare is streamlining repetitive administrative tasks — from charting and coding to summarizing prior visits. This reduces clinician workload, shortens documentation cycles, and increases throughput, allowing care teams to serve more patients with the same headcount.
These efficiency gains represent just one of many high-impact applications of ChatGPT that are redefining how healthcare organizations operate at scale.

Faster clinical decision-making
By surfacing insights from unstructured data in seconds — think chart summaries, treatment guidelines, or outcome predictions — ChatGPT accelerates how quickly providers can evaluate and act on clinical scenarios. It excels at identifying recurring patterns in medical histories and surfacing relevant context, giving clinicians better grounding for diagnostic or treatment decisions without combing through every note manually.
Reduced documentation burden
AI-powered note generation, coding suggestions, and real-time transcription relieve providers from the “after-hours charting grind.” Instead of manually drafting every clinical note, clinicians can rely on ChatGPT to capture the most relevant data while preserving medical intent. The result: fewer burnout symptoms and more face time with patients.
Increased patient engagement and satisfaction
For ChatGPT for healthcare professionals, one of the biggest wins is offloading routine patient communication. Patients can ask about dosages, upcoming procedures, or therapeutic guidance using natural language, and get consistent, accurate answers 24/7. These conversational touchpoints help build emotional intelligence into digital care delivery while supporting elders or those with limited health literacy.
Cost savings across care delivery
From reducing claim denials to lowering administrative overhead, ChatGPT delivers measurable savings. It can also automate common patient interactions — like prescription refills, appointment reminders, and pre-visit instructions — reducing inbound call volumes and freeing up staff time.
Enhanced scalability of care teams
Virtual assistants, triage bots, and ambient scribes let clinicians “delegate” more routine tasks to AI, enabling leaner teams to serve more patients without sacrificing quality.
24/7 availability without burnout
Unlike human staff, ChatGPT doesn’t need breaks. It can offer empathetic, consistent support around the clock — whether answering FAQs or guiding patients through complex instructions.
Accelerated innovation and research
By scanning and summarizing vast medical literature, ChatGPT shortens the time from hypothesis to discovery. It also aids in identifying gaps in data and care delivery that fuel R&D.
More equitable access to information
ChatGPT supports translation of complex medical jargon into plain language and operates in multiple languages, helping bridge gaps for non-native speakers and individuals with lower health literacy. It can function with limited internet connection using local caching strategies, expanding usability in rural clinics.
By promoting better awareness of symptoms, treatments, and patient behavior trends, it empowers underserved communities to participate more fully in their care journey.
Recommendations for Using ChatGPT in Healthcare
There are numerous ways in which ChatGPT can be utilized in healthcare beyond the examples we have discussed. As technology advances, we anticipate even more innovative applications and high-quality health bots.
However, it’s important to note that ChatGPT is not intended to replace human healthcare providers. Although it can provide helpful assistance, it should always be used in combination with the knowledge and judgment of trained professionals.
And when it comes to giving out professional medical advice, you should tread lightly. It’s super crucial to train the bot on verified medical data and double (if not triple) test everything. Leaving room for human healthcare providers in patient interactions is always a good idea. We’ll provide more details on the resonsible use of ChatGPT for medical applications in the next section.
In general, LLM technology has undeniable potential benefits in healthcare, and we can expect to see further progress in this field. While there may be challenges to overcome, the potential rewards make it worthwhile.
Aslo read: Medical Record Automation Guide
Challenges of Developing a ChatGPT-Powered Health App
There’s no use in adopting ChatGPT for healthcare services if we’re not planning a unique, proprietary application that’s differentiated enough to gain traction. We can’t just make a front end for patients and providers, connect it with an off-the-shelf ChatGPT instance and expect a comprehensive, engaging user experience, can we?
To justify the use of ChatGPT in healthcare applications, we need to respond to a few challenges.

Bringing your chatbot up-to-date
As you probably already know, OpenAI language models were trained on publicly available data up to September 2021. Therefore, we’d need to bring it up-to-date with current knowledge. Fortunately, we don’t need to cover the whole spectrum of global knowledge and instead focus on our particular use case.
- feed in information from the web
When setting up a database for training our bot, we can crawl the web, gathering all relevant content that will help us get the chatbot up to speed. The apparent upside is that we can keep updating this information in the background as new knowledge becomes available.
- connect to specialized APIs
It’s a good idea to also train the ML algorithm by feeding it data from healthcare APIs. For example, we could use openFDA API, an open-source API for drug-related information. Or we can also rely on commercial APIs like Mayo Clinic API for symptom checking. By leveraging these AI tools, we can expedite the development process, making the integration of health-related information more efficient and accurate.
- connect to patient records: labs, DNA, etc.
Other data sources include EHRs that can be platform-agnostic, like Epic or Allscripts, or Apple’s Health Records. Chat GPT in the healthcare industry is incredibly useful for scanning large data chunks and fishing for relevant information.

- fine-tune the model with documents and research via embeddings
Finally, we can use the embedding technique to upgrade the knowledge graph of our chatbot and improve its responses based on new or modified info.
Making a chatbot unique
Besides bringing the ChatGPT’s language model up-to-date with the most recent facts by connecting it to external data sources, we also need to utilize whatever moated, proprietary knowledge we have based on our medical research and associated patient data.
Related: A Complete Guide to Building a Chatbot
We can make our healthcare app unique by training the chatbot on proprietary data and applying exclusive business logic (stemming from actual medical practice). That’s how we make the most of ChatGPT for healthcare analytics capabilities, leveraging its generative AI-powered insights to uniquely tailor our app, enriching patient care, and advancing medical research.
Comprehensive user experience
Another pitfall when considering ChatGPT use in healthcare is to view it as a response generator rather than a virtual assistant blending in with the other app features. For example, an e-pharmacy app with embedded ChatGPT could consult on multi-drug interactions and provide e-commerce options right in chat. Or ChatGPT can help users schedule appointments, making it a seamless part of the overall user experience and not just a standalone feature.
If you think about it, many still consider chatbots a text interface where patients or providers need to type in requests and read answers. However, interfaces can adjust based on a use case, and we can see a few other options:
- speech to text
A spoken request can be parsed by an add-on AI algorithm and passed onto the ChatGPT engine for further processing.
- text to speech
A bot can reply with voice in a similar fashion.
- file generation
Providers could find it helpful when a chatbot can generate a report as a downloadable file based on requested information.
- forms, infographics, etc.
We may also explore other ways of interacting with the chatbot by introducing forms, e.g., to simplify data entry for patients. The latest ChatGPT-4 model can also analyze infographics, which can be put to use, too.
The issue with these conversational interfaces is that you can’t test them entirely using a typical rapid prototyping approach. If you remember, we love prototyping at Topflight to validate design ideas before starting to code. With chatbot apps, we might need to consider no-code prototypes that allow more in-person testing.
Unique development process and technical chops
Developing ChatGPT healthcare applications is a little different than creating a regular app. Of course, the front ends are more or less the same, although caution is required if you choose a text-to-speech variant. So what’s different?
First, since the app exploits ChatGPT uses in healthcare, we’re dealing with machine learning software development. This implies training and fine-tuning data models, which then need to be scrutinized by a QA team.

Of course, a production-level health app cannot afford hallucinations still common to ChatGPT (at least in its default incarnation). For example, during research for this blog, the AI pal sent me a fake science article at nature.com, which I had to double-check (the bot claimed it could analyze X-rays) and then make ChatGPT admit its forgery.
So, we pay special attention to testing and QA cycles. We also want to automate this process at least partially, just like we do on other projects.
Another area calling for attention is the DevOps pipeline. The LLM models we train require a separate DevOps pipeline that should sync with the rest of the DevOps environment responsible for compiling the front ends and the rest of the code. It becomes a matter of mastering specific supplementary frameworks and tools, such as vector databases like Pinecone or Weaviate.
Related: DevOps Implementation Roadmap
Where do I actually start?
When looking for ways to apply ChatGPT in the healthcare industry by building a healthcare app, you follow the same steps as with other software development projects. I mean, at least on a high level — when you’re just starting and need to frame the business idea.

To remind you, the software development routine includes the following stages:
- discovery: identify the prominent use cases; set ROI targets; research the target audience and appropriate frameworks; define requirements for the MVP.
- prototyping and design: create a validate the user experience in graphics.
- create a proof of concept: work with an LLM to see if it helps you reach business goals.
- work on an MVP: design, development, and testing of a minimum viable product that can start generating traction.
- release and maintenance: you release the product and keep updating it when you think you’ve verified a product-market fit.
Read up on the steps for building your own ChatGPT chatbot in a separate blog.
Technically speaking, when developing an artificial intelligence product, you must start experimenting with a language AI model as soon as possible. You can make do with default interfaces because, at this point, you want to validate a bot’s responses.
That said, I encourage you to contact experts as early as the discovery step. For example, our strategy is to follow and assist our partners every step of the way from the very beginning — as long as they’ve got a sound business idea for Chat GPT in the medical field.

HIPAA Compliance Concerns
Since we’re building a healthcare app, it must adhere to HIPAA security standards, including administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to protect the privacy of protected health information (PHI).
Related: HIPAA Compliant App Development Guide
Naturally, this includes ensuring that third-party service providers, such as OpenAI for ChatGPT APIs, comply with HIPAA requirements.
No out-of-the-box compliance
Unfortunately, OpenAI does not currently offer HIPAA compliance for their language model APIs, as their terms of service expressly prohibit the use of ChatGPT APIs for any purposes that are “regulated by U.S. federal or state laws or regulations relating to the privacy, security, or handling of personal data, including but not limited to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).”
Here’s how to solve that
Therefore, if your healthcare app is subject to HIPAA requirements, you must find an alternative solution for your ChatGPT functionality that is HIPAA compliant or work with OpenAI to establish a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) to ensure that their services meet the necessary HIPAA requirements. To qualify for this, you must have an Enterprise Agreement with OpenAI and a qualifying use case.
Alternatively, you may consider hosting a ChatGPT model on your own servers, which may allow you greater control over the security of PHI.
Besides, we can always pull out a proven HIPAA implementation best practice that already works in many other healthcare products we’ve developed: patient data anonymization.
Another workaround is to revert to Microsoft’s Azure Open AI Service, which provides additional controls over data privacy.
Finally, we can always opt for using open-source LLMs that we can customize and deploy as we see fit to fully comply with the HIPAA requirements.
What’s Next for ChatGPT in Healthcare?
Let’s take a look at what’s ahead for ChatGPT in healthcare.
IoT edge deployment
The deployment of small language models on edge, i.e., into low-power IoT chipsets, could have significant implications for remote patient monitoring. By deploying ChatGPT models onto medical sensors, patients can receive real-time feedback and medical advice without relying on a doctor’s physical presence. This could be particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions who require continuous monitoring.

Work with graphical data
ChatGPT-4’s ability to work with infographics could improve patient understanding of medical information. By being able to interpret and explain infographics, ChatGPT-4 could help patients make more informed decisions about their health. It could also assist healthcare professionals in conveying complex medical information in a more accessible way.
Indeed, this strategic utilization of ChatGPT for medical professionals signifies a meaningful stride towards enhancing patient education and fostering proactive healthcare.
Medical education
The use of chatbots in medical education could have a significant impact on the healthcare industry. By providing personalized education and training, chatbots can help healthcare professionals and medical students stay up to date on the latest medical research and techniques. They can also help patients understand their medical conditions and treatment options, improving potential health outcomes.
Tense competition
As new players enter the field, competition in the healthcare AI market will likely intensify. MedPaLM, an AI medical chatbot developed by Google, is one example. The increasing number of AI-powered healthcare solutions on the market could lead to improved patient care and outcomes, but it could also make it more challenging for providers to choose the best solution for their needs. Right now, ChatGPT in medicine holds a very lucrative promise for professionals.

Less red tape
Another potential use case for ChatGPT in health care is to assist providers with bureaucratic tasks. This could include generating patient letters, discharge summaries, and referral letters. By automating these tasks, ChatGPT can help providers save time and reduce administrative burden, allowing them to focus more on patient care. Additionally, ChatGPT-generated letters can ensure accuracy and consistency, reducing the risk of errors in communication between providers and patients.
Topflight’s Experience with ChatGPT in Healthcare Apps
We had extensive experience developing chatbots assisted by AI long before the ChatGPT trend emerged.
Mental health chatbot with custom AI engine
For example, we created a mental health chatbot to help individuals maintain emotional health and improve their time management, decision-making, and goal-setting. Users input their daily emotions (journaling) via chatbot conversations, respond to questions, and like or dislike recommended articles and famous quotes.
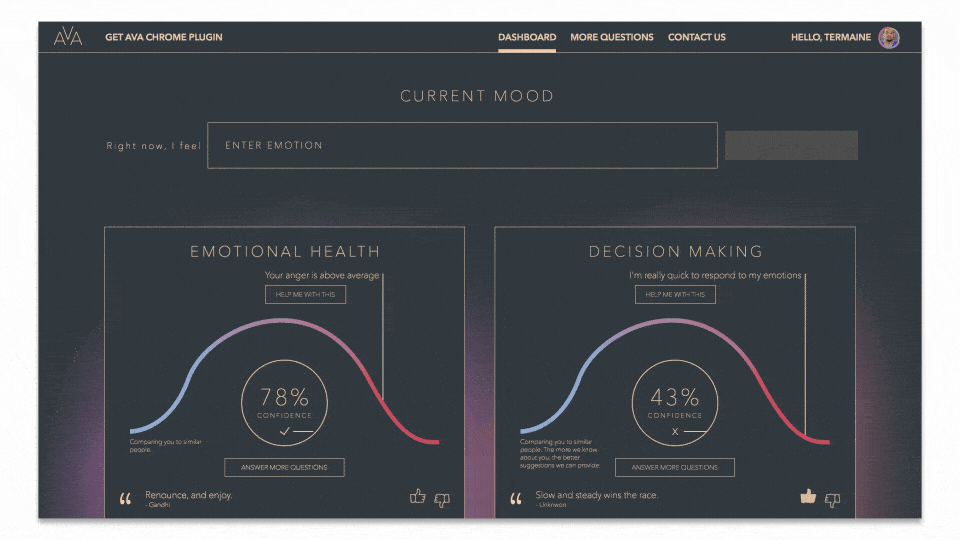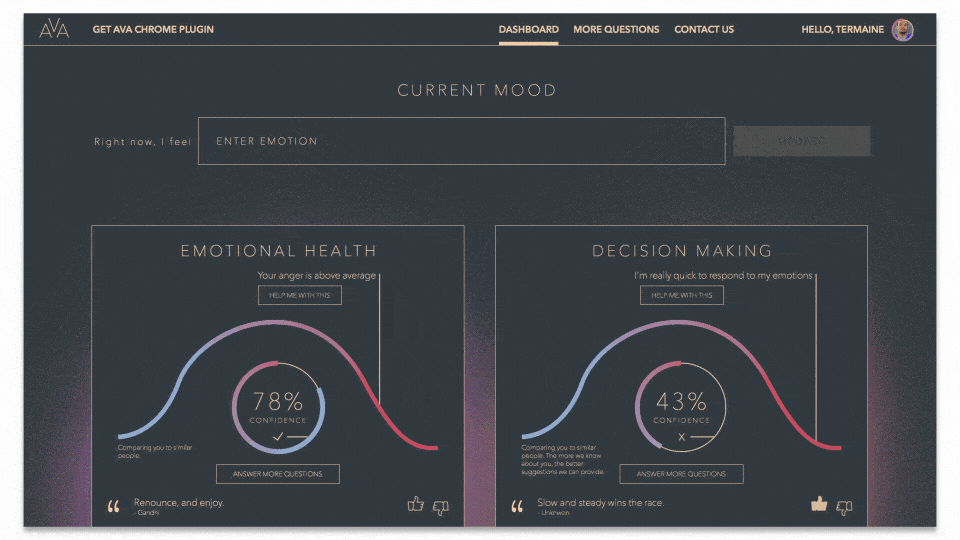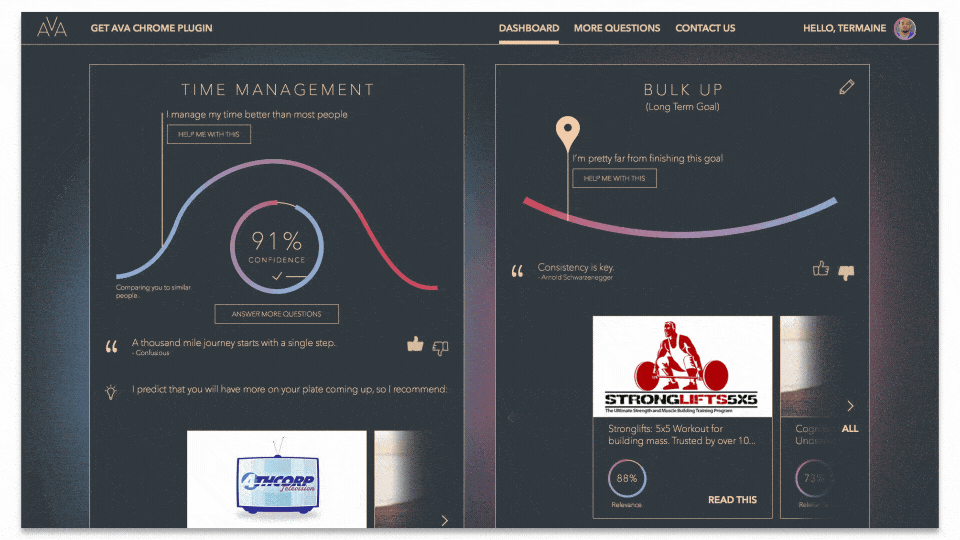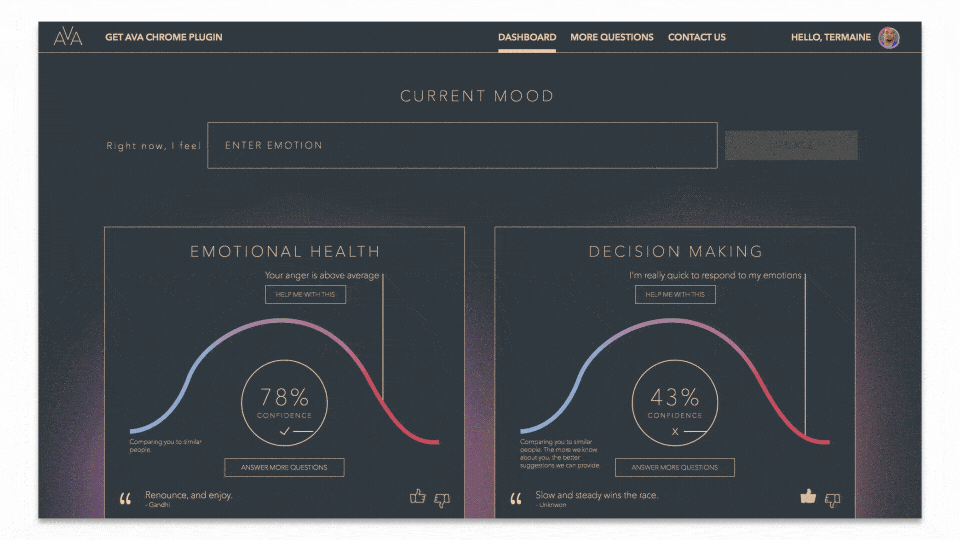 The recommendation system we built integrates two types of machine learning platforms (a K Nearest Neighbors algorithm and Restricted Boltzmann Machine). It learns about users and content in real-time to improve the accuracy of recommendations, classifications, and predictions. Check out the corresponding case study for more details.
The recommendation system we built integrates two types of machine learning platforms (a K Nearest Neighbors algorithm and Restricted Boltzmann Machine). It learns about users and content in real-time to improve the accuracy of recommendations, classifications, and predictions. Check out the corresponding case study for more details.
Real-World Projects That Integrate ChatGPT
Everybody’s trying to adapt ChatGPT use cases for healthcare — but the most meaningful results are already emerging from real-world deployments, not hypotheticals.
Our AI developers were early adopters of the OpenAI APIs for ChatGPT, and we’ve since moved from demos to production. One example: GaleAI, an intelligent coding platform that processes thousands of medical notes in seconds, boosting reimbursement accuracy and eliminating hours of manual work for billers. Another: Mi-Life, a HIPAA-compliant voice assistant for caregivers, delivering personalized consults using patient health data while reducing medication errors and staff burnout.
These tools show how teams can integrate ChatGPT not only into mental health apps but also into back-office automation and frontline care delivery.
Get in touch if you’re looking for more ChatGPT healthcare examples or need help bringing your health app idea to life using OpenAI’s technologies.
[This blog was originally published on 12/25/2023, and has been updated with more recent content]
Frequently Asked Questions
Is ChatGPT secure for handling patient data?
Yes, ChatGPT is designed with privacy and security in mind. The platform does not provide HIPAA compliance out of the box, which requires strict data privacy and security standards for healthcare providers. However, we can use security best practices to protect PHI, for example, data anonymization.
How does chatGPT compare to other AI chatbots in healthcare?
ChatGPT is one of the most advanced AI chatbots available for healthcare applications. It has outperformed human physicians in diagnosing medical conditions and providing treatment recommendations.
How can healthcare providers integrate chatGPT into existing systems?
ChatGPT can be integrated into existing healthcare systems through API integration. Healthcare providers can work with ChatGPT developers to customize the chatbot to their specific needs and incorporate it into their existing workflows.
Are there any ethical concerns with using chatGPT in healthcare?
As with any AI technology, there are ethical concerns with using ChatGPT in healthcare. One concern is the potential for bias in the data used to train the model. Additionally, there are concerns about the use of AI in decision-making and the potential for AI to replace human judgment.
How can healthcare providers ensure ?
Healthcare providers should be transparent with patients about the use of chatbots powered by ChatGPT and the purpose they serve. Providers should also ensure that patients have access to other forms of communication if they prefer not to use the chatbot. Additionally, providers should ensure that patients understand the limitations of the chatbot and that it is not a replacement for in-person care.
How is chatGPT used in healthcare?
The top use cases we’ve identified include disease diagnosis, predicting medical outcomes, personalized medicine, patient education, mental health support, remote patient monitoring, drug discovery, clinical trial matching, EHR management, chatbot assistants for healthcare providers, and medical education.


