Hi, I’m Siri, Alexa, Cortana, Meena … With new chatbot gals springing to life non-stop, I bet there are a slew of domain-hunters bulk-buying all sorts of amy.coms, hoping to strike gold when you come up with a brand-new chatbot.

I can’t promise a catchy brand name, but we can discuss how to make a chatbot app while adding value to your business.
This post will walk you through the essentials of creating chatbots, whether for customer engagement or automating specific tasks.
Key Takeaways
- The chatbot market promises to reach $10.08 billion by 2026 on a global scale. Hence, the gold rush to code a chatbot among enterprises and startups.
- How to make a chat bot capable of keeping up intelligent conversations? Use AI technologies like GPT-3 or TensorFlow.
- Three main reasons to create a chatbot are to mine customer data, save time on customer service and back-end operations, and make your brand accessible 24/7. For instance, developing a chatbot tailored to automate customer support can save significant time and resources.
- An essential part of AI chatbot development is training a bot with sample and real-life data.
- The seven steps that answer the question “How to build a chatbot?” include choosing a channel (custom-built vs. messenger-based), identifying the most-fitting tech stack, prototyping, designing the UI, training, testing, and deploying the bot.
Table of Contents
- Types of Chatbots
- Chatbot Features
- The Role of AI
- Out-of-the-box vs. Custom Solutions
- Top 3 Chatbot Platforms
- Step 1: Identify the type of chatbot you are building
- Step 2: Select a channel
- Step 3: Choose the technology stack
- Step 4: Design the conversation
- Step 5: Train the bot
- Step 6: Test the chatbot
- Step 7: Deploy and maintain the bot
Chatbot Market Overview
Before we sail on this exciting journey, it wouldn’t hurt to know what’s happening in the chatbot market these days. Understanding the market can guide you as you plan to implement a chat bot for your business needs.
The Present and Future of Chatbots
Even though Facebook’s M, Microsoft’s Tay, Google’s Allo, and a few other interactive agents have already passed away since the initial chatbot frenzy of 2016, many believe we’re in a chatbot renaissance era today.

Despite initial frustration with chatbot limitations, data shows that this market is still in its infancy with close to 90% of funding deals occurring at early-stage rounds. According to the latest CB Insights’ report in the post-COVID world, the chatbot market is currently estimated at $7.7 billion.
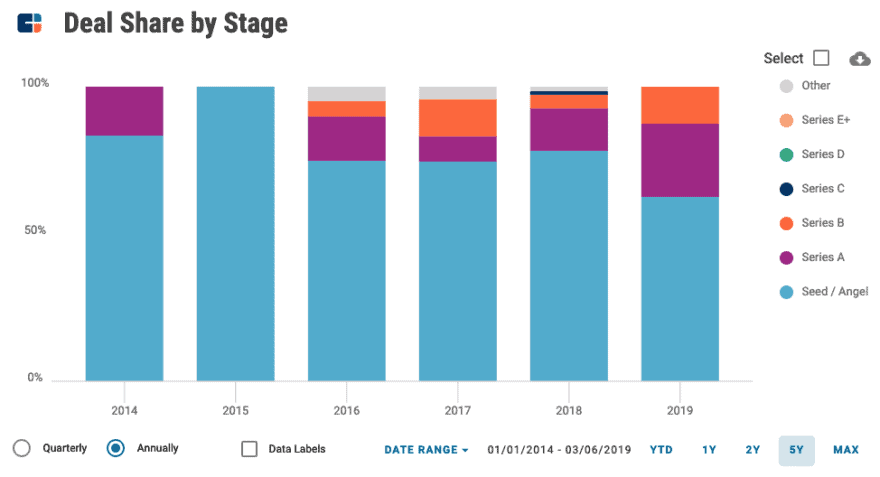
And the future looks promising too: Gartner claims that chatbots will be “the most important platform paradigm” for enterprises by 2021. If that sounded overly optimistic in the pre-COVID reality, today, that certainly resonates with the remote business model that’s on the rise.
And the $11 billions that bots can deliver in annual cost savings for retail, banking, and healthcare by 2023 suddenly begin to look more realistic. Here are a few mind-boggling stats about talkbots:
- More than 50% of enterprises will prioritize development of chatbots over mobile apps by 2021 / Gartner.
- Bots will handle $112 billion in e-commerce transactions by 2023 / Juniper Research.
- The global chatbot market will reach $10.08 billion by 2026 / Globe News Wire.
Chatbot Trends
Chatbots flooding messengers
If you think about it, a messenger is an ideal environment for a chatbot. What is a chatbot if not a digitized dialog between a person and an aspiring bot?
Virtual agents can be found practically on any platform, including web and mobile, but messengers are where they really thrive. In 2018, there were more than 300,000 active bots on Facebook Messenger, and I’m sure Mark Zuckerberg will report around 500,000 at the next conference. In fact, most chatbot app development takes place on instant messaging platforms.
Banking, healthcare, and retail will spearhead chatbot adoption
CB Insights expects financial, healthcare, and retail sectors to continue driving chatbot growth in the post-COVID world due to business lockdowns and social distancing measures. And it’s hard to argue, given that customer service and sales processing are the prime use cases for bots. Healthcare bots, naturally, get a lot of use these days too, before forwarding users to a virtual call center.
Related: Healthcare App Development
Banking App Development: The Complete Guide
AI breakthroughs
Conversational agents are also getting smarter. OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research laboratory, has recently released a new language learning model (GPT-3 and then GPT-4) that can enable any chatbot to engage in human-like conversations. These self-learning conversational agents can save 2.5 billion customer service hours for businesses and consumers by 2023.
Another exciting contender in the space that revolutionizes content creation with cutting-edge AI technology is MagicWrite, developed by Canva and powered by OpenAI. The AI feature empowers users to effortlessly generate captivating and persuasive content within seconds. With a wide range of formats available, including social media posts, blog articles, and resumes, MagicWrite suggests the best wording and phrasing based on user prompts. It also allows customization of tone, style, and length to suit individual needs. That’s a remarkable example of how you can take a ChatGPT model and make a beautiful product out of it.
Ready-made solutions like Canva’s MagicWrite and custom-built AI bots can become a game-changer for anyone regularly involved in content creation, delivering high-quality results quickly and efficiently.
Related: ML App Development Guide
Payments
Since chatbots are becoming the entry point for your customers to learn about your products and services, providing a bots payment option seems inevitable. You can hook your bot with an external payment provider like Stripe or Facebook Pay.
Related: P2P App Development Guide
Voice-driven chatbots
Various reports and studies indicate that chatbots will likely become predominantly voice-controlled experiences in the near future. Capgemini’s study in 2019 revealed that customers would prefer to use voice for the whole buying journey: from product/service research to payment and customer service.
Also read: Guide to Building Mental Health Chatbots
Chatbots at workplace
Gartner believes that 70% of office employees will interact with bots in their daily routine on a regular basis by 2022. Imagine asking a chatbot at your workplace to fetch you that report from a couple of months ago instead of trying to locate it in your local or cloud environment yourself.
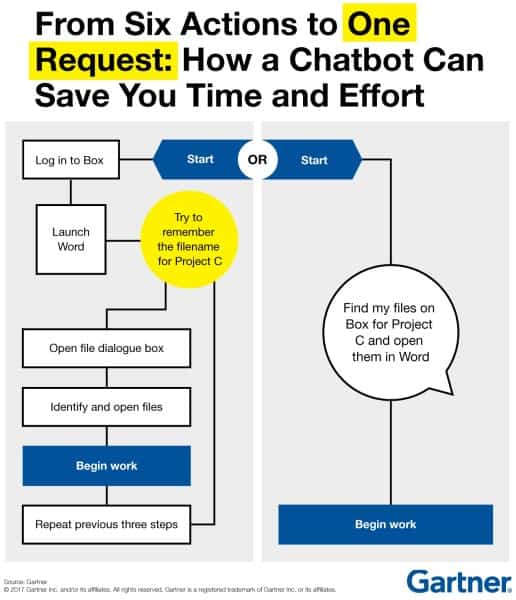
Low-code / no-code bots
The rise of the citizen developer movement has not left the bot industry untouched.
Check out our article about the difference between No-code/Low-code and Programming
Chabot Benefits: Three Reasons to Make Your Own Chatbot
The recent pandemic has shown the true value of having a chatbot. They are ready to assist customers across all venues even when front desks are swamped, and few businesses are open for visits.
Reason #1: Make your brand interactive and accessible 24×7
The most apparent advantage that businesses can achieve with a talkbot is making their services available for customers worldwide, around the clock. The bot will take site visitors through all the steps of a buying journey or help them answer their queries.
Chatbots can simultaneously handle thousands of customers without slowing down, taking a break, or slipping an error. What’s more, they keep getting smarter in the process.
Reason #2: Mine customer data
The way bots get smarter over time is by analyzing user inputs. You can use this data to optimize online and mobile experiences for your customers, for example, by bringing the information and products they are looking for closer to them.
Reason #3: Optimize back-end operations
Then, you can deploy a chatbot to streamline your internal workflows. JP Morgan managed to squash 360,000 hours spent by lawyers reviewing loan contracts down to mere seconds once they had deployed a contract processing bot.
Types of Chatbots
You have probably run into a few bots yourself; when asking your smartphone to set the alarm or when visiting a website outside office hours. These are different types of bots. Let’s go over the most popular types to see which one suits your business model.
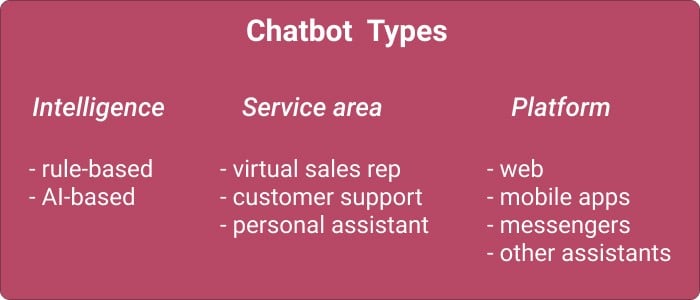
Some businesses prefer a basic chatbot for handling common queries, while others opt for advanced models for specific tasks.
Intelligence
From the intelligence viewpoint, there are “dumb” and smart chatbots. The former rely on rules, coming up with responses based on a rigid script, and their intelligent counterparts can support quite intelligent conversations.
- Rule-based chatbots
- AI-based conversational bots
Conversational chatbots rely on AI algorithms and machine learning to process your inputs and make their replies more personal, relevant to your context. With rule-based bots, you have to pick answers yourself or rely on their best guess at the keywords you used in your inquiry.
Area of application
If we look at the most common service areas for bots, we’ll notice they are beneficial in support, sales, and as personal virtual assistants. You can often see chatbots serving customers and helping them make purchases in the retail sector.
- Virtual sales representatives
- Customer support
- Personal assistant
As for assistants, those are mostly cutting-edge solutions offered by tech giants, e.g., Apple’s Siri or Google’s Meena. These virtual assistants feature voice control and keep developing as they learn more about you.
Some would argue they are hardly chatbots, but come to think of it — you interact with them through dialogs, and, frankly, their competence is the yardstick for every conversational bot out there. Of course, the cost of creating a chatbot akin to such voice assistants is crushing to most startups. However, integrating with them is a viable option.
Platform
Finally, you can distinguish between bots depending on the platform they dwell on: whether this user experience is for a website or a mobile solution.
Some of the most popular places are instant messengers like Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, Telegram, and Kik.
- Web
- Mobile apps
- Messengers
- Existing assistants like Alexa or Google Assistant
Some chatbots exist in the form of standalone mobile apps. That’s often the case when you need them to do a little more than merely fetch some information. There are way more chatbots for websites and messengers — that’s where most customer service and ecommerce salesbot hang around.
It’s worth noting that a bot may often exist on all these platforms to reach a wider audience.
Finally, Siri, Alexa, and other supercharged bots take the form of voice platforms that permeate entire ecosystems. Here’s the latest neural conversational model from Google in real time – Meena that will soon migrate to all possible devices and platforms:
Related: Choosing the right tech stack for your platform
Chatbot Features
What do your customers expect from a chatbot? Find them a healthcare provider for a consultation? Rule out a preliminary diagnosis? Or advice on getting their finances in order? Siri, Alexa, and the likes set the high bar for user engagement, but let’s see what a modern chatbot can offer users.
Cross-channel seamless communication
Customers expect to have the same seamless experience with your bot regardless of where interaction occurs: in a browser, mobile app, messenger, or even inside Google Assistant. So make sure to set up a chatbot as a platform-independant solution.
Rich messaging
Being able to reply with images and links makes your bot more utilitarian. This feature is especially in demand with retail chatbots to help customers find products.
Integrations with external systems
If your conversational agent is integrated with the rest of your infrastructure, it can save you hours of work on mind-numbing manual activities like CRM updates, accounts balancing, etc. So write a chatbot presuming it will need to work with various software via APIs.

Actions
The best thing about chatbots is to give them orders, like sending an email or finding that old message with the tracking number.
Human handoff
Let’s admit that there are still cases when a bot can be helpless. Such scenarios should include an option for handing off a conversation to a human agent.
Accessible
Just like with web and mobile app development, accessibility should be top of mind when developing a bot: keyboard navigation, zoom in, support for screen readers, etc.
Secure
Of course, a chatbot needs to adhere to cybersecurity best practices, given they can now execute payments and handle PHI. So, HIPAA, PCI, and other regulations apply.
Related: HIPAA compliant video conference and messaging SDKs/APIs
Related: HIPAA Compliant App Development: Steps, Processes, Features
Analytics on the backend
And last but not least, your bot should be piling up data in the background for further analysis as it chatters with your customers and employees.
Remember that essential features of a chatbot include natural language processing, contextual understanding, and seamless integration with existing systems. When you build a chat bot, incorporating these features ensures it can generate responses effectively while maintaining user satisfaction.
The Role of AI
I’m sure that as an entrepreneur, you understand that the point of AI in bot technology is not to pass the Turing test. It’s all about serving people with niche requests, helping them as much as possible without human intervention. AI plays an important role across different industries – fitness, fintech, healthcare.
Related: Fitness App Development Guide , Fintech App Development Guide
The idea is to occupy your sales and support staff with really challenging tasks.
What do we usually expect from a chatbot? Get us a booking, fetch an FAQ article, get our contact details — all of these are pretty simple and do not require much AI. But if we dare to converse with a bot to pre-diagnose a minor disease or ask for financial advice, we need to know it really has some smarts. How do you program a chatbot like that?
In the latter case, a chatbot must rely on machine learning, and the more users engage with it, the smarter it becomes. So every successive conversation becomes more effective. As you can see, building bots powered by artificial intelligence makes a lot of sense, and that doesn’t mean they need to mimic humans.
Read more on conversational AI in healthcare.
Out-of-the-box vs. Custom Solutions
Today, there’s no shortage of tools for creating intelligent agents; pretty much every chatbot builder allows you set up an off-the-shelf chatbot. Such bots are usually effective for niche tasks, like fetching customer order details and displaying the order status or booking a meeting with a specialist.
Choosing between ready-made chatbot solutions and custom-built ones depends on your business needs. Custom solutions allow you to create chatbots designed to address unique challenges, while off-the-shelf options may serve basic needs.
When it comes to building conversational bots that need to take into account user data and the context, you are better off building a custom app solution that you can train with sample data.
Top 3 Chatbot Platforms
A chatbot platform is a toolset for building talkbots. There are quite a few out there: You may come across blogs talking about 175 chatbot platforms.

And if you take into account that companies like Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft, and IBM also have taken their stake in the conversational AI technologies, it may be hard to pick a cutting-edge chatbot platform that makes sense for your business.
It’s worth noting that these bigger companies offer chatbot frameworks (not platforms). Frameworks like Amazon Lex or IBM Watson allow you to build various text- and voice-powered chatbots and advanced virtual assistants without dictating the UI component. They just give you access to the AI dialog engine that you are free to use at your discretion. Simply put, they are more than chatbot platforms.
Without trying to make a choice for you, let us introduce you to a couple of iconic chatbot platforms (and frameworks) — each unique in its own way.
Chatfuel
This platform often makes it to the top lists for its simplicity and a free subscription option. You don’t need developers or any prior knowledge of how to create a chat bot with Chatfuel.

Platforms: Facebook, Instagram, and Messenger.
Highlights: No-code solution. Powers over a billion conversations every month.
Competition: ChattyPeople, Botsify, ManyChat.
Dialogflow CX
Dialogflow CX is part of Google’s Dialogflow — the natural language understanding platform used for developing bots, voice assistants, and other conversational user interfaces using AI.

Platforms: Cross-platform. Can be used with your custom bots as a back-end processing unit.
Highlights: Gives you the power of Google Cloud and Deep Learning.
Competition: Lex by Amazon, Microsoft Bot Framework, IBM Watson.
RASA
RASA is an open-source framework for building bots. Much like with Dialogflow, you can create an AI chatbot with text and voice interactivity and rely on the open-source machine learning potential.
Platforms: Cross-platform, including web, messengers, and a few other chatbot frameworks.
Highlights: You will need to host your bots yourself. Requires advanced developer skills.
Competition: Botkit, Botpress.
How to Develop a Chatbot From Scratch in 7 Phases, Step by Step
Let’s go through all the necessary steps of the custom chatbot development methodology so that you can end up with a purpose-driven, profitable bot. Here’s our take on how to develop an AI chatbot. You’ll notice that the steps follow the typical software development process but also have some nuances.
To successfully create a chatbot app, following a step-by-step process ensures clarity and efficiency throughout development:
| Step | Description | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify the Type of Chatbot | Define the purpose and functionality of your chatbot. | – Determine if it’s rule-based or AI-driven. – Identify key use cases (e.g., support or sales). – Align the bot’s purpose with customer needs. |
| 2. Select a Channel | Choose the platform(s) where the chatbot will operate. | – Decide on single or multi-channel strategy. – Ensure compatibility across platforms like websites, Messenger, or apps. – Use a unified chatbot stack for consistency. |
| 3. Choose the Technology Stack | Select the framework or platform for development. | – Evaluate open-source vs proprietary options. – Ensure integration with existing systems. – Consider NLP libraries for advanced capabilities. |
| 4. Design the Conversation | Develop the chatbot’s interaction flow and user experience. | – Map out dialogue paths and replies. – Use DIY platforms for simple flows or frameworks for advanced UX. – Collaborate with chatbot developers for complex designs. |
| 5. Train the Bot | Prepare the chatbot to understand user intents accurately. | – Use datasets like emails or support tickets for training. – Leverage third-party datasets for additional knowledge. – Refine intent recognition through iterative training. |
| 6. Test the Chatbot | Evaluate the chatbot’s performance with real users. | – Conduct user testing for diverse scenarios. – Implement fallback responses to direct users. – Address edge cases and optimize functionality. |
| 7. Deploy and Maintain | Launch the chatbot and ensure ongoing optimization. | – Integrate with systems like CRM or ERP. – Monitor performance and refine answers. – Update features based on user feedback and analytics. |
Step 1: Identify the type of chatbot you are building
Why are you building a chatbot? What are you helping to achieve for your customers or prospects? Answers to these questions will guide your choice of a bot type. During the setup phase, it’s critical to define your bot’s purpose, whether it’s for handling text messages or answering FAQs.
As we’ve mentioned before, it can be a rule-based chatbot with predefined answers or an advanced AI-enabled bot that keeps learning from user input.
Today’s two most popular uses are support — think a FAQ bot that can fetch answers to any questions, and sales — think data gathering, consultation, and human handoff.
Step 2: Select a channel
You will need to follow your prospects and make the chatbot available on the platform that they are most comfortable with. Will it be a bot hosted on your site, a standalone mobile app, or a Facebook Messenger bot? It’s up to your customers and prospects.
Remember that you may opt for a multi-channel strategy, in which case it’s preferable to use the same chatbot stack across all the platforms as opposed to, say, having a sales bot built with Chatfuel for Messenger and using Dialogflow for Google Assistant and mobile app versions.
Step 3: Choose the technology stack
When you know what customer problem you’re solving and target platforms, you may begin choosing your bot’s technology stack. You can pick one of the frameworks and have chatbot developers design your bot, or get your hands dirty with one of the DIY talkbot-building platforms.
When you pick a framework, your choice will probably be driven by the developers’ skills and the availability of open-source and third-party libraries for NLP (natural language processing), such as ChatterBot. Just ensure that the library or SDK you choose integrates well with your existing software systems.
At the core of every chatbot lies its ability to understand and process language inputs, which is often achieved using advanced language models designed for natural language processing.
Other questions you should ponder during chat bot development:
- Will this technology allow me to expand into voice-driven chatting?
- Is this a proprietary or open-source library?
- What is the developers’ market for this technology right now?
Step 4: Design the conversation
Once you’ve selected a tech stack, you can build the chatbot by designing the conversation flow. If you do this with one of the DIY platforms, the process is almost as simple as drag-and-dropping reply options.
However, if you’ve picked a framework (to ensure AI capabilities in your chatbot), you’re better off hiring a team of expert chatbot developers.
They will build out the front and the server-side of the chatbot. One thing you don’t need to worry about is UI: A dialog is a dialog; there’s not much you can change in your chatbot’s graphical UI when you use a bot platform.
At the same time, if you proceed with a framework, you can come up with any UX.
Step 5: Train the bot
If you’ve built a simple chatbot based on rules, you can skip right to step 6, but if your bot uses AI, you first need to train it on a massive data set. Basically, what you want is for the bot to understand the user intent, and that is done by teaching the bot all the different variants that customers can ask for things.
Ideally, you achieve that by training your bot on some existing data sets, such as emails, support tickets, etc. And the alternative is to get a third-party data set with the information that your bot needs to know, e.g., Question-Answer Dataset, The NPS Chat Corpus, or any of these 15 chatbot datasets for machine learning.

Step 6: Test the chatbot
As with any software product, you’d want your bot to converse with real humans to see if it can really help them. Remember that chatbots are still a novelty, so many of your customers will try to break it. Therefore, it’s best if you foresee these scenarios with graceful general replies that direct conversation towards actual goals or with a frictionless fallback to a human agent.
Step 7: Deploy and maintain the bot
Deploying a chatbot often doesn’t take a ton of time. You just need to ensure that all endpoints are connected, and the bot is integrated with your entire infrastructure if you happen to use a CRM, ERP, or similar software systems. Once the bot is deployed, the chatbot development life cycle doesn’t end. Now you need to check the statistics and refine answers to keep users happy.
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Chatbot?
The cost of developing a chatbot varies based on its complexity and the features required. For example, chatbot creation for e-commerce purposes may cost less than building a multi-language AI-powered bot.
You can build a basic rule-based chatbot free of charge, but anything that scales well and relies on any AI at all will start with a budget of $30,000 or so. It’s unlikely that you’d want to take on Alexa, Siri, or other big gals, but if you are building a serious ML-driven chatbot, app development costs can hover well over $99,000.
Also Read: AI App Development Guide, How To Build Your Own ChatGPT Chatbot
Creating Bots with Topflight Apps
Some of the chatbots we’ve recently developed include standalone mobile app SoberBuddy, available for iOS and Android, and a mental health bot, built as a progressive web app.
Related: Advantages of PWA Over Native Apps
With SoberBuddy, we inherited the project from a previous team that struggled to turn the app into an engaging, revenue-generating experience. And so we had to clear the mess.
One of the big decisions we did was replacing a Dialogflow architecture with a custom rule-based conversational structure. That helped us to rule out many bugs and unnecessary complications.
Today, we continue working on SoberBuddy, turning it into an effective instrument for self-help groups. The web interface we are building on the back-end will allow group admins to track their members’ performance.
Here’s the case study if you’d like to learn more about this project.
As for Xzevn, it’s an AI-enabled talkbot that interacts with individuals learning about their mental conditions and recommending them appropriate content to improve their mental health.

The case study here lays down the details if you’d like to learn more. Also check out our article on developing a mental health app.
If you think you could use a friendly conversation about building chatbots powered by AI without being judged, just book a spot here. We’re app developers in Miami and California and will be happy to chat with you (no bots on the call, promise). Let’s create your own chatbot!
Related:
[This blog was originally published in September 2020, and has been updated for more recent data]
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know if my chatbot is effective?
You should integrate it with an internal CRM to track conversion, or see if the chatbot you’re looking to build offers analytics on its back end.
What is the difference between chatbot building platforms and frameworks?
A framework provides instruments for developers to make an AI chatbot. And platforms can be operated by someone with zero coding experience. Plus, a chatbot platform is usually an all-in-one solution that provides you with everything you need to build a chatbot, unlike a framework that may contain just the NLP engine or other parts.
Where will my chatbot reside once it's built? It is necessarily a mobile app?
It can be a JavaScript plugin on your site, a separate chat in a messenger app (which itself can live on web/mobile/desktop) such as Facebook Messenger, or it can live in Alexa or Google Assistant. Finally, it can be a standalone mobile app.
How long will it take to create a chatbot?
We can build an MVP within a couple of weeks, and a full-fledged chatbot with a custom UI may take several months.
What's the cost to build a chatbot application?
From our experience, an average bot’s cost varies between $30,000 and $60,000.



