Today, we can spin up a mobile app and start training with a virtual coach providing real-time feedback personalized to our performance. Or we can take a CT scan and get our diagnosis almost immediately. The groundbreaking image-processing technology that makes these and other similar interactions possible is computer vision.
Keep reading to learn more about fascinating applications of computer vision in the medical field.
Top Takeaways:
- Computer vision in healthcare will be a $1,398.47 million market by 2025
- The technology has matured to the point where it’s successfully employed at clinics and hospitals
- Consumer-centric medical applications of CV start gaining real traction with such tech giants as Amazon, Google, and Microsoft joining the game
Table of Contents
- What Is Computer Vision in Medicine
- What Are The Tasks of Computer Vision in the Medical Field
- Main Advantages of Using Computer Vision in Healthcare Applications
- Use Cases of The Applications of Computer Vision in the Medical Field
- Building Blocks of CV-Based Applications
- Our Expertise in Healthcare Computer Vision
What Is Computer Vision in Medicine
Computer vision (CV) is the technology that allows a computer — whether it’s a smartphone, smart glasses, or some medical device — to recognize images and videos and make sense of their content.
In action, computer vision in medical applications may look as simple as, e.g., taking a picture of a pill and getting an instant recommendation on drug interactions. However, there’s a lot of AI (artificial intelligence) processing taking place on the inside.
In its purest form, computer vision in medicine is machine learning algorithms that have been trained to recognize particular objects and their attributes in a medical image. These algorithms can also work in tandem as neural networks, continuing to sharpen their precision while recognizing more training data samples.
This particular type of neural networks that get smarter over time is called deep learning, a subset of the machine learning discipline.
Coupled with modern advanced mobile cameras, such AI code turns computer vision into one of the fastest developing technologies, which holds a lot of potential for healthcare applications.
Not surprisingly, the market affirms that medical computer vision is here to stay. The global market of computer vision in healthcare is forecasted to grow to USD 1,398.47 million by the end of 2025. That’s quite a healthy compound annual growth rate of 23.18% from 2019.
Related medical device integration and medical device cost breakdown
What Are The Tasks of Computer Vision in the Medical Field
Let’s think about different kinds of applications of computer vision in the medical industry. Two things immediately come to mind: professional and mass consumer use cases.
By professional use cases, I mean healthcare professionals employing computer vision to serve patients better. A mass consumer scenario is when patients use computer vision-enabled software to reach their health goals on their own.
How computer vision in healthcare aids professionals
Let’s look at some of the most common computer vision applications in the healthcare industry.
Diagnosing
Computer vision has become indispensable in providing early diagnoses and improving the overall diagnostic efficiency of healthcare facilities, and an essential part of healthcare app development services. Machine learning algorithms help process various medical imagery, including CT scans, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), ultrasound, X-rays, computed tomography, etc.
Not only can the technology do such analysis at scale, but it can also discern patterns in the imagery that no human eye can distinguish, and that helps doctors with diagnosing diseases at early stages.
Example: Viz.ai reduces the timeframe for delivering stroke care treatment by 1.5 hours for each patient.
Reports automation
Reports automation can be thought of as a side-effect and a powerful feature of analysis that computer vision algorithms produce. Once imagery is processed, computer vision-powered software transfers all data and examination results to other healthcare systems.
Patient condition assessment
Another area for applying computer vision in medicine is the detection of a patient’s condition. Healthcare providers can train software to accurately determine the mental and physical state of patients.
Example: Triton, an iPad app installed in the operating room, automates the tracking of blood loss during surgical procedures. The app measures how much blood stays on surgical sponges after a C-section procedure.
Clinical trials
Computer vision-enabled mobile apps can help care providers verify if patients participating in a study take the prescribed medicine and follow the treatment. The best part is the whole monitoring process is automated, which means no time is lost on manual verification.
Example: AiCure helps researchers control whether patients adhere to their prescribed treatments.
Read more on clinical trial software development
Surgery assistance
Surgeons can use a combination of computer vision and AR technologies mounted into smart glasses to get directions during surgical procedures.
Example: TouchSurgery automatically pulls benchmarking analytics from surgical videos and anonymizes sensitive video frames before saving a recording to the cloud.
Miscellaneous non-medical applications
Hospitals can also deploy computer vision solutions to monitor and keep stock of inventory, instantly add handwritten information to healthcare systems, or simplify in-door navigation.
Some experts also raise the question of using computer vision for tracking healthcare professionals’ activities. One such example could be autonomous tracking of hand hygiene.
Consumer-centric computer vision use case
Now let’s see how patients can use human-sight simulating solutions to their advantage.
Medicine detection
When you think about patients using computer vision software, the first thing that comes to mind is an app that helps identify meds and provide details on drug interactions.
Example: Pill Identifier is a drug reference guide that helps customers identify the brand and generic drugs by name.
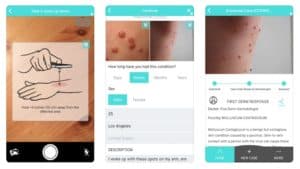
Preliminary research
Another common way the technology can aid patients is during the preliminary research when they try to identify the health issue they deal with.
Example: Google has recently demoed its AI app for diagnosing common skin conditions.
Fitness & recovery therapy
Pose & movement estimation and detection is an excellent example of machine learning algorithms at work, helping customers complete physical exercises correctly. Or the technology can be used for elderly fall detection.
Example: Amazon’s training app Halo measures users’ activity, sleep, tone of voice, and body composition.
Assistance to visually impaired people
Computer vision is also used by people with vision impairment to navigate in unfamiliar environments. Computer vision for medical imaging can work with sensors like Apple LiDAR to create a virtual map of the surrounding area and describe it to the user.
Example: OrCam Eye helps visually impaired people read texts, recognize faces, shop, and work more efficiently by conveying visual information audibly, in real-time, and offline.
Main Advantages of Using Computer Vision in Healthcare Applications
What are the main benefits of the application of computer vision in healthcare?
Value-based care
Since the technology removes manual work for doctors, they can spend more quality time with patients and help more people within the same timeframe than they did without machine-powered eye-sight solutions.
Accurate early diagnosing
The fact that computers can hold and process an immense amount of data gathered from previous examinations allows them to quickly discern indistinguishable anomalies. That leads to physicians detecting illnesses at early stages when treatment is very efficient.
Improved outcomes for patients
Patients obviously get better outcomes because they receive faster and more accurate care. For example, CV software’s classification accuracy of brain tumors has already reached the level of certified clinical experts.
Also Read: Medical Large Language Models: Bridging the Gap between Technology and Healthcare
Use Cases of Applications of Computer Vision in the Medical Field
Let’s quickly skim through the medical disciplines where machine vision offers the most value.
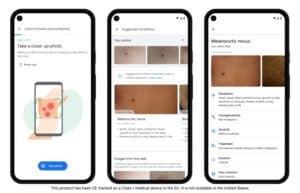
Dermatology
Computer vision helps identify benign lesions and track lesion growth and color changes.
Different studies have shown that machine learning algorithms can classify malignant skin lesions from benign lesions on par with board-certified dermatologists.
Radiology
X-rays, CT, and MRI present a perfect case for machine vision. Radiologists rely on algorithmic neural networks to automate disease classification and image segmentation, enhancement and reconstruction, automated report generation, and temporal tracking.
Cardiology
Machine vision in cardiology is mainly used for diagnosis and screening by automatically analyzing cardiac ultrasound and echocardiograms. The technology has proven its efficiency across various medical settings: from acute inpatient facilities to emergency rooms to outpatient centers.
Surgery
Surgical applications of AI-powered image analysis mainly revolve around video analysis. The technology allows to assess surgeons’ skills and provide them with real-time contextual prompts. That’s achieved with a real-time pattern recognition technique.
Pathology
Cancer detection (e.g., lung cancer or breast cancer) is one of the primary uses of AI-assisted computer vision in pathology. Pathological analysis, which generally involves visual inspection, can be very subjective due to the limitations of human visual perception.
Therefore, trained image recognition algorithms support healthcare professionals’ decisions in diagnostics, prognostication of outcomes and treatment response, and disease monitoring.
Ophthalmology
In ophthalmology, computer vision can reliably diagnose several conditions, including glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular degeneration, childhood blindness, etc. In addition, machine algorithms can predict nonocular information, e.g., anemia and chronic kidney disease, from eye images.
Building Blocks of CV-Based Applications
Computer vision for healthcare is a burgeoning field today. Fortunately, we don’t have to rebuild the technology ground-up every time we need to build an application bearing image recognition features.
There are quite a few digital solutions on the market that can be integrated with custom-developed solutions, for example:
- OpenCV
- Cloud Vision API by Google
- Microsoft Computer Vision
- IBM Watson
Tech giants offering these tools make them HIPAA compliant, so you don’t have to worry about that. Instead, you need to ensure that a tool covers the use cases you envision in your application. Support for your platform of choice (web, mobile, desktop) is also equally important.
Using these off-the-shelf instruments and other open-source CV libraries, we can build computer vision software significantly faster.
Our Expertise in Healthcare Computer Vision
One of our notable medical projects is Allheartz, an AI-driven platform that leverages computer vision to enhance physiotherapy and sports care. By analyzing patients’ movements through their mobile devices, Allheartz enables remote therapeutic monitoring, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving recovery outcomes. Our role involved complete development of the platform and computer vision algorithms to accurately assess exercise performance, providing real-time feedback to both patients and healthcare providers.
If you have an idea of a healthcare computer vision application, schedule a call to discuss its implementation with our experts.
Related Articles:
- How to create a physiotherapy app
- How to develop a skincare app
- Healthcare Cloud Computing Guide
- How to start a healthcare startup
- Healthcare App Development Guide
- How to create a telehealth app
- Python in Healthcare: Use Cases and Best Practices
[This blog was originally published on 6/16/2021 and has been updated with more recent content]
Frequently Asked Questions
How much will it cost to build, let's say, a skin analyzing mobile app that would work in iPhone or Android apps?
Around $125,000 if you have an extensive dataset of images for training algorithms. An MVP should fit within $80,000.
Are there available tools for building mobile machine vision applications?
Yes, for example Apple offers the Vision framework that performs face and landmark detection, detects text, scans barcodes, and offers general feature tracking.
How long does it take to develop a healthcare computer vision application?
It takes an incredible amount of resources to build an AI-vision solution from scratch, whereas with ready-made machine vision libraries you can expect something tangible within 4-5 months.