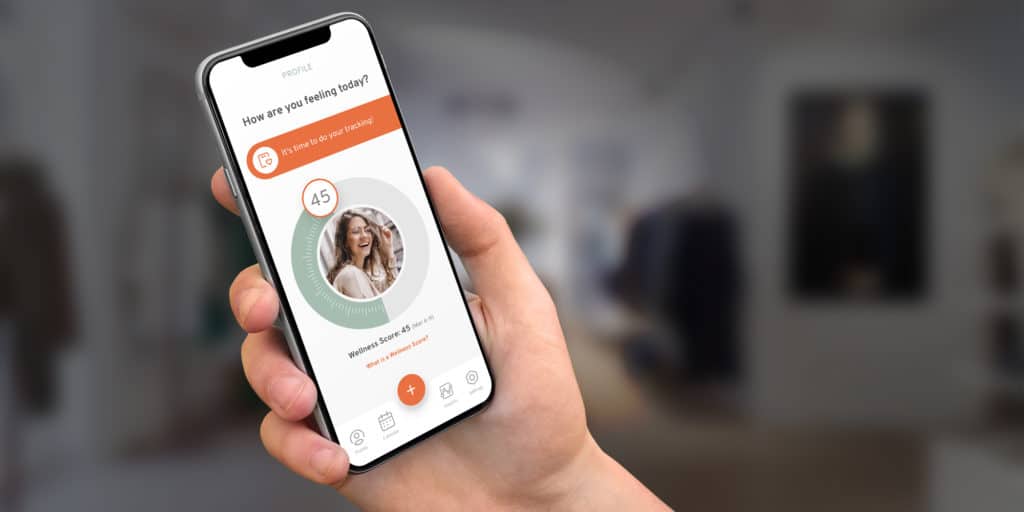
The United States isn’t “running out of doctors” in a dramatic way—it’s running out of capacity in a measurable one. The Association of American Medical Colleges projects a shortage of 13,500 to 86,000 physicians by 2036. At the same time, access gaps aren’t limited to primary care: HRSA’s shortage-area data shows ~137M people live in designated Mental Health HPSAs (as of Jan 1, 2026).
That’s the real backdrop for this telehealth app development guide. Done right, telehealth apps don’t just “add video visits”—they stretch clinical teams with smarter scheduling, asynchronous touchpoints, triage, and workflows that reduce wasted clinician minutes (the most expensive unit in healthcare).
This telemedicine app development breakdown shows how to develop a telemedicine app—from must-have features and security/compliance basics to the build steps, integration choices, and cost drivers that actually move the budget.
Top Takeaways:
- The global telehealth market reached $186 billion in 2025 and is projected to hit $219 billion in 2026 (Fortune Business Insights), making it one of the fastest-growing segments in digital health and driving sustained demand for telemedicine app development.
- There are plenty of ready-made video-calling and chatting tools like Agora and PubNub available to expedite telehealth app development.
- The cost of custom developing a telehealth app may vary from US$59,000 and all the way to US$149,000, and requires extensive planning right from figuring out platform and tech stack to UI/UX design and maintenance.
1. What are the Latest Telemedicine Trends in 2026?
2. Practical Applications of Telemedicine in Healthcare
3. What Challenges Do Telehealth Apps Face?
5. What Functions Do You Need and What Tools Can You Use?
6. How Do I Build a Telehealth App Step by Step?
7. How Much Does it Cost to Build a Telehealth App?
8. White Label Telemedicine Solutions
9. How Topflight Fast-Tracks Telehealth App Success
What are the Latest Telemedicine Trends in 2026?
The COVID-19 pandemic transformed healthcare services faster than a decade of shiny consumer tech ever did. But the “everyone is doing video visits” phase is over. In 2026, the real story is that virtual patient care has normalized into a set of repeatable workflows—especially where access is tight, follow-ups are frequent, and no one wants to burn clinician time on low-value logistics.
That shift matters if you’re planning telemedicine application development or deciding whether to create a telehealth app now: the winners aren’t “video-first,” they’re “workflow-first.” Think scheduling that actually reduces friction, async intake that removes back-and-forth, and routing that keeps the right patients out of the wrong queues. (Your clinicians don’t need more meetings. They need fewer. Telehealth just happens to be the lever.)
Market Overview
From a market lens, the telemedicine market is still expanding globally: Fortune Business Insights estimates $186B (2025) and projects $219B in 2026.
In the healthcare sector, utilization looks less like a spike and more like a steady baseline. FAIR Health’s claims-based tracking shows that in early 2025, about 14.9% of patients had a telehealth claim in January, dipping slightly to 14.5% in February (commercially insured). And behavioral health remains the heavyweight: the American Hospital Association reported behavioral health represented 67% of telehealth encounters in 2024 (commercially insured).
Practically, that demand shows up in three dominant modalities you’ll need your telemedicine software to support: live phone consults, live video consults, and health app or website consults (asynchronous messaging/intake plus lightweight monitoring). Audio-only also isn’t going away—Medicare policy explicitly allows two-way audio-only in defined scenarios (and permanently for behavioral/mental telehealth).
Net: if you’re trying to build a telemedicine system in 2026, treat modality as a product decision (not a UI toggle) and plan telehealth platform development around workflows, not “video visit features.”
More on health and fitness app development in our dedicated blog.
Telehealth Market Statistics
US, 2024–2025 baseline → planning for 2026
| Metric | What the numbers say | Context (why it matters) | Source / As-of |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price reality (commercial claims) | $24 median allowed (telehealth) vs $24 (in-person office) | Telehealth wins on workflow + access—not automatically on “cheaper visits.” | FAIR Health (US), Dec 2024 |
| Baseline utilization | 5.04% of all medical claim lines were telehealth | Not a spike—an operating baseline you can design around. | FAIR Health (US), Dec 2024 |
| Behavioral health dominates | 66.9% of telehealth volume was behavioral health; 58.5% of telehealth patients had a mental health condition | If your product doesn’t support BH workflows well, you’re building “telehealth” with one hand tied behind your back. | Trilliant Health (2024); FAIR Health (Jan 2025) |
| No-show impact | Lower odds of non-attendance: OR 0.61 | Show-rates are operational ROI. Less wasted clinician time, fewer reschedules, tighter panels. | Systematic review/meta-analysis (45 cohort studies) |
| Speed to care | Avg wait: 1.80 days (phone) / 2.29 days (video) vs 3.52 days (in-person); within-1-day: 66.61% (phone) vs 46.49% (in-person) | Telehealth’s quiet superpower is throughput: shorter lead times and faster routing. | (US study in report) |
| Satisfaction (virtual care) | J.D. Power score: 730 (direct-to-consumer) vs 708 (payer-provided), out of 1,000 | Consumers reward convenience + clarity. “Workflow-first” is also “experience-first.” | J.D. Power, 2024 |
| Modality mix (reality check) | Physician video use: 49.6% (2024) vs 59.1% (2020); 40.9% provide audio-only weekly | Build around multiple modalities as distinct workflows—not a video toggle in settings. | AMA, 2024 |
| RPM economics (Medicare) | $110–$140/month per patient reimbursement potential; payback estimate 3–5 months (large practices, 10+ physicians) | RPM ROI depends on ops + scale. The “app” is the easy part; the workflow is the business. | (Medicare/RPM notes in report) |
| Hospital-at-Home (when ops are tight) | Reported savings 19%–30% vs inpatient (Johns Hopkins); ROI mixed across operators | Shows where telehealth is heading: protocolized, hybrid care models—not “video visits.” | Johns Hopkins (reported); broader evidence mixed |
Telemedicine is Inclusive
Underserved communities, seniors with chronic diseases, and other vulnerable groups of population along with tech-savvy younger people looking for a healthy lifestyle — a vast population is going to adopt and rely on telemedicine. But here’s something to ponder: what about the ‘pain points’ these diverse groups might encounter while using a telemedicine platform? Are we ready to address those to make their telemedicine experience smooth and user-friendly?
That means the companies working on telemedicine solutions would need to sort out another layer of complexity with telemedicine software development. How do you create a telemedicine app that is equally well understood and navigated by different target audiences?
Check out our on demand webinar on: Buy or Build Telehealth?
Vertical Growth
Telehealth is rapidly expanding beyond e-consulting with a physician. As patients are getting accustomed to the new technology, there appears the need to cover the whole spectrum of healthcare services. That brings to life new, niche telemedicine products, such as teledermatology apps, telenursing apps, telepsychiatry, teledentistry, and other types of health related virtual care apps.
Better Insurance Coverage
Insurance companies and federal health care programs are stepping up to cover care administered by means of telehealth apps. For instance, Medicare already covers some types of telemedicine services and remote patient monitoring. Note that you can build a telemedicine platform integrated with insurance services. Isn’t it exciting to see how mobile health is transforming not just our access to medical care but also how we manage our insurance needs?
Read Also: Insurance App Development Guide
Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring (RPM), as a distinct subset of telehealth, is garnering wider adoption as providers seek to push back patient readmission rates. RPM apps have proven their effectiveness in helping doctors watch patients’ recovery or illness progression while they stay at home, in a remote care setting.
Related: Guide to Building a Remote Patient Monitoring app
AI
Artificial intelligence is a change agent. Applied to patient healthcare data, the technology can assist medical personnel by making predictions about patients’ well-being. That results in timely and accurate treatment plans.
Related: Deep Learning in Healthcare: Use Cases and Case Studies, AI App Development Guide
Benefits of Telemedicine Apps
Why would you build a telemedicine app for Android and iOS? Training a new doctor can take up to 18 years. And one of the benefits of telemedicine is that it eliminates this waiting period for patients in communities with limited access to healthcare professionals by linking them to other physicians from all over the country, on-demand.
Let’s look at some other benefits telemedicine has to offer for patients and care providers (especially, in a mobile healthcare aspect).
Patient Benefits
-
-
- On-demand access to healthcare specialists
- Authorized permission to message the doctor
- No need to travel to a clinic
- Lower cost of service
- Ease of use (accessible on any device)
-
Provider Benefits
-
-
- Freedom to collaborate with remote colleagues on patient cases
- Access to home-care and discharged patients
- Ability to treat more patients simultaneously
- Integration with EHR and other clinical systems
- Fewer cancellations and missed appointments
-
Telehealth solutions need to be built by a specialized custom mobile apps development firm that understands healthcare regulations.
Top 3 Successful Telehealth Apps
Before you build a telehealth application, let’s review some notable incumbents in the field for inspiration.
Teladoc
Market Cap: ~$1M (down from $12.2b in 2002)
Founded in 2002, Teladoc is one of the most established publicly traded telemedicine companies in the US. The company provides patients and doctors with easy-to-use mobile apps for iOS and Android and offers its telehealth platform as a white-label solution.
The Teladoc notable app features include:
-
-
- Scheduling a meeting
- Mobile payments
- Video and audio calls
- Integration with Healthkit and Google Fit
- Medical history
-
Doctor On Demand

Doctor on Demand is a telemedicine app that connects patients with a variety of healthcare professionals. Similar to Teladoc, the company offers its customers apps on both mobile platforms. Patients can schedule a video appointment from their phones and tablets.
Notable features:
-
-
- Upfront pricing
- Medication management
- Push notifications
- Video calls
- Healthkit and Google Fit
-
Related: How to Develop a Doctor’s Appointment App, On-Demand Doctor App Development
MDLIVE
Funds raised: $124m
MDLIVE is a telehealth service company that was founded in 2009 in Sunrise, Florida. MDLIVE is a serious player in the telemedicine space, especially after it partnered with Walgreen’s to step up its meds prescription options.
Important features:
- ePrescribe integration
- Video calls
- Health records
- Instant messaging
- Mobile payments
Related Article: The Best Telemedicine Apps
Of course, there are many other types of healthcare apps with telemedicine features that focus on different care aspects (therapy, psychology, etc.), but we won’t cover them all here for the sake of brevity.
Practical Applications of Telemedicine in Healthcare
The impact of telemedicine extends far beyond virtual consultations. By integrating digital tools, telehealth is transforming how clinics and hospitals operate, enhancing doctor-patient relationships, and streamlining treatment workflows.
These applications ensure that therapists, general practitioners, and specialists can deliver more accessible, efficient, and personalized care.
How Telemedicine is Transforming Clinics and Hospitals
Telemedicine is reshaping healthcare institutions by optimizing workflows and improving patient outcomes:
- Virtual Consultations – Enables remote diagnosis and follow-ups, reducing congestion in hospitals and clinics.
- Integrated Pharmacies – Patients can receive digital prescriptions and have medications delivered without visiting pharmacies in person.
- Remote Therapy Sessions – Therapists can conduct video consultations for mental health support and rehabilitation.
- Chronic Disease Management – Continuous monitoring and digital check-ins improve treatment adherence for long-term conditions.
Enhancing Doctor-Patient Relationships Through Telemedicine
The adoption of telemedicine strengthens communication between doctors and patients, making healthcare more responsive and engaging.
Through doctor profiles, patients can easily review a provider’s experience and specialties before scheduling appointments. Reminders for upcoming sessions, medication adherence, and follow-ups improve patient compliance. Additionally, telemedicine platforms track consultation duration, ensuring that both parties have sufficient time for discussions without disruptions.
Streamlining Treatment with Telemedicine Solutions
Hospitals and private practices benefit from automated processes that enhance personalized care and treatment efficiency:
- Diagnostics Integration – Remote patient monitoring tools collect vital signs and share real-time data with healthcare providers.
- AI-Powered Symptom Analysis – AI chatbots assist in preliminary assessments before connecting patients with specialists.
- Centralized Health Records – Ensures seamless access to patient history, improving decision-making in hospitals and outpatient facilities.
By leveraging telemedicine, healthcare providers can offer a more patient-centric approach, optimizing services while maintaining high standards of care.
What Challenges Do Telehealth Apps Face?
Telehealth isn’t “emerging” anymore — it’s operational. But the moment you try to move from a pilot to a real telehealth app (or a full telemedicine platform), the hard parts show up fast: compliance, call quality, patient UX, and integrations that don’t politely stay inside your sprint plan.
The good news: most of these problems are predictable. Below is a practical challenge-to-solution map we use when building telemedicine apps so teams can design for reliability and scale from day one — instead of patching fires in production.
| Challenge | What it looks like in real life | Solution (what you build) | Build notes (so it doesn’t blow up later) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HIPAA compliance complexity | “We’re using cloud… are we compliant yet?” | Encrypt PHI in transit + at rest, role-based access, audit logs, retention controls, BAAs with vendors | Decide where PHI lives early; audit logging is hard to bolt on later |
| Video quality complaints | Frozen video, choppy audio, “I can’t hear you” | Adaptive bitrate + auto quality fallback; pre-call network test; audio-only fallback | Instrument call quality metrics; add TURN relay fallback for restrictive networks |
| High no-show rates | Clinicians waiting; patient forgets / can’t join | Reminders (SMS/email/push), calendar invites, one-click join, easy reschedule | Add “join from reminder” deep link + quick device permissions check |
| EHR integration difficulties | “We need Epic/Cerner/Athena integration” (but requirements are fuzzy) | Start with FHIR where possible; isolate integration layer; queue + retries; mapping/normalization | Scope the first integration to 1–2 workflows (e.g., demographics + encounters) |
| Patient identity matching | Duplicate records, wrong charts, safety risk | Strong identity model + verification steps; matching rules; manual review workflow | Patient matching is a product problem, not just an API call |
| Security & account takeover | Weak passwords, reused links, session hijacks | MFA options, short-lived tokens, session timeouts, device trust, rate limiting | Don’t rely on “magic links” alone for sensitive actions |
| Consent & privacy expectations | Patients ask “Who can see this? Can I revoke access?” | Consent capture + revocation flow; granular sharing; clear privacy UI | Make consent auditable (who consented, when, to what) |
| Clinical documentation burden | Clinicians hate “double charting” | Smart templates, structured notes, auto-attach visit metadata, exportable summaries | Optimize for “finish the note fast,” not “more fields” |
| Accessibility & UX friction | Older patients can’t navigate; low vision/hearing | Large-tap UI, captions support, keyboard navigation, screen-reader friendly flows | Test with real devices + real patients, not just your dev team’s iPhones |
| Language barriers | Miscommunication, safety risks | Multilingual UI; interpreter workflow; real-time captions where feasible | Don’t use generic translation for medical instructions without review |
| Scheduling & time zones | Wrong appointment times; missed visits | Time zone–safe scheduling, buffer rules, clinic hours logic, cancellation policy | Prevent double-booking with server-side rules (not only front-end checks) |
| Scalability & reliability | Peak-hour slowdowns, dropped calls | Observability (logs/metrics/traces), autoscaling strategy, graceful degradation | Build SLOs early: “video works” isn’t a metric—define it |
HIPAA compliance isn’t a feature — it’s the floor. If your telehealth app touches Protected Health Information (PHI) — imaging like MRIs and CT scans, doctor’s notes, lab results — you need to be HIPAA compliant end-to-end, including vendors. In practice, teams often start with HIPAA-aligned hosting on AWS or GAE, then add audit logging and access controls early (because retrofitting “who accessed what, when” later is a special kind of pain).
And no, “just use Skype” isn’t a plan: Skype has not signed a BAA, and you shouldn’t treat consumer video tools as a secure telehealth app replacement.
Related: Building a HIPAA Complaint App Made Easy
Telemedicine App Security
As telemedicine adoption continues to grow, ensuring the security of patient data is paramount. Healthcare applications handle vast amounts of sensitive information, making data privacy and HIPAA compliance non-negotiable. Any security concerns in a telemedicine app can lead to data breaches, exposing patient data to cyber threats.
Ensuring Security in Telemedicine Apps
To safeguard telemedicine applications, developers must implement the following measures:
- Data Encryption: End-to-end data encryption ensures that sensitive medical information remains protected, both at rest and in transit.
- HIPAA Compliance: The app must adhere to HIPAA regulations, securing protected health information (PHI) and limiting unauthorized access.
- Secure Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and biometric verification enhance access control.
- Regular Security Audits: Routine assessments help identify vulnerabilities and prevent potential data breaches.
- Role-Based Access Control: Restricting access ensures that only authorized personnel can view or modify patient data.
Best Practices for Telemedicine App Security
Building a secure telemedicine application requires adherence to industry guidelines and best practices:
- Security Testing: Perform penetration testing and vulnerability scans to detect weaknesses before deployment.
- Data Storage Protections: Store PHI in secure, encrypted databases with access logging and monitoring.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Implement real-time threat detection to counteract cyber threats proactively.
- Compliance with Future Regulations: Stay updated on evolving data protection laws to ensure long-term security.
Telehealth Compliance Checklist
(practical implementation checklist; requirements vary by org + state)
HIPAA Requirements (program + technical controls):
☐ BAAs in place with all vendors that may touch PHI (cloud, video, messaging, analytics, support tools)
☐ Encryption in transit (TLS) and at rest for PHI
☐ Audit logs for PHI access (who/what/when/where) + log retention defined
☐ Role-based access control (RBAC) + least privilege (minimum necessary access)
☐ Strong authentication (MFA for clinicians/admins; secure session management)
☐ Automatic session timeout / re-auth for inactive sessions (set a policy; 15 minutes is a common starting point, not universal)
☐ Data retention + deletion policy (define by legal/clinical needs; don’t hardcode one number unless you’ve standardized it)
☐ Backups + disaster recovery plan (RPO/RTO targets documented)
☐ Incident response plan + breach notification workflow tested
☐ Regular risk assessment + vulnerability management (pen tests/scans, remediation SLAs)
State-Specific Requirements (operational + clinical rules):
☐ Provider licensing verification for patient’s location at time of visit
☐ Cross-state practice rules (telehealth modality allowed, supervision rules if applicable)
☐ Consent requirements (telehealth consent language, when/how it must be captured)
☐ Prescribing rules (controlled substances, tele-prescribing constraints, PDMP checks where applicable)
☐ Minor consent / guardian rules (varies heavily by state and service type)
☐ If recording is used: recording consent + storage/retention policy + access controls
By prioritizing telemedicine app security, developers can build trust among patients and healthcare providers, ensuring that virtual care remains both effective and secure.
What Functions Do You Need and What Tools Can You Use?
In order for your app to deliver complete telehealth services, you need to have the following basic features on your telemedicine app. Depending on whether you start with a minimum viable product (MVP) or continue building a full-fledged telemedicine app, there will be different features in your app.
MVP Feature Set
An MVP version of a telemedicine app needs to provide users with bare-bones features, just enough to turn virtual care into reality. Let’s briefly review this essential functionality and the benefits of healthcare solutions of this type.
Secure Video Calling
This is the most important service of the app. Patients and providers need to see and talk to each other securely in real-time which is where HIPAA compliant video conferencing and messaging come into play (a must for all healthcare applications dealing with PHI). Visual cues make a big difference in identifying signs of illness. The video needs to be of high quality with low latency.
Also, you may be interested in how to build a video chat app.
Related: Build a Video Calling Application
Peer-to-Peer Chat
Providers and patients must have the ability to send rich messages to each other to exchange information before, during, and after a call. This is a useful tool for healthcare providers to give written instructions and reach their patients when not able to call.
Also, patients can write information that can’t be easily understood during a call due to differences in pronunciation or interruptions in network connectivity. Or they could schedule appointments via secure messaging.
Also Read: Guide to building a messaging application
Backend Database
If you are building an app for neurology, you will need a secure repository for patient information, medical history, labs, and imaging. This will also handle user authentication.
Appointment Scheduling
An appointment tool or patient scheduling tool so people can book appointments with their chosen provider. Correspondingly, if the user can book an appointment, the admin staff should be able to manage appointments (cancel, reschedule, etc.) and sync bookings with major calendar applications.
Data Encryption
Do you ever wonder about the safety of your personal data when using a healthcare mobile app? How secure is your personal health information, such as your heart rate, when it’s being transmitted over the internet?
Well, there’s good news! One of the key features of our telemedicine app is Data Encryption. This feature ensures that your personal health information is always protected, providing the highest level of privacy and security.
Doctor Profiles and Personalized Patient Management
A doctor profile feature ensures that healthcare providers have a dedicated space to showcase their expertise, credentials, and availability. This enhances trust between patients and doctors while making it easier to select the right specialist.
Similarly, patient profiles store essential medical history, past consultations, and prescribed medical treatment, providing a convenient way to access crucial health information in one place. By offering a structured overview of a person’s health journey, this feature enables seamless communication and informed decision-making between providers and patients.
For clinics and hospitals, an app for doctors should include intuitive dashboards, appointment tracking, and secure data access, ensuring efficient patient management while maintaining compliance with industry regulations.
Those are the core features of any basic telemedicine app, but what about other telemedicine app features that will make your solution stand out?
MVP Scoping Guide: Integrate EHR + Scheduling + Payments Now, or Later?
(Rule of thumb—this is about sequencing to avoid scope blowups, not “one right answer.”)
1) Are you launching into an existing clinic workflow where the EHR is the system of record from day one?
→ Yes: Plan EHR integration early (otherwise you risk “double charting” backlash)
→ No / greenfield or DTC: Defer EHR; go to #2
2) Will clinicians/staff need scheduling to run in the app (self-serve booking, reschedule, reminders), not handled by front desk tools?
→ Yes: Ship scheduling in MVP (missed visits and time-zone bugs become your new hobby)
→ No: Start with manual scheduling / simple appointment requests, integrate later
3) Do you need to collect payment inside the product at launch (cash-pay per visit or subscription)?
→ Yes: Ship payments in MVP (keep it simple; optimize “pay → join call” flow)
→ No / billed elsewhere (insurance, invoicing, existing billing ops): Defer payments; integrate later
4) If you answered “Yes” to EHR integration: is your requirement “we need Epic/Cerner/Athena integration” but the workflows are still fuzzy?
→ Yes: Don’t “integrate the EHR.” Integrate 1–2 workflows first (rule of thumb: demographics + encounters) and expand after pilots
→ No (clear workflows + mapping): Proceed with a phased EHR integration plan
What this usually means in practice
-
Visits-first MVP (most common): video + chat + basic scheduling; payments only if you’re cash-pay; EHR later
-
Clinic-embedded MVP: scheduling + identity model + narrow EHR integration early; video/chat still core
Build notes (so it doesn’t blow up later)
-
Start with FHIR where possible, isolate the integration layer, and design for queue + retries + mapping/normalization
-
Treat patient matching as a product workflow, not “just an API call”
Advanced Feature Set
Going beyond MVP with its key features, you may start adding features that further improve the quality of care and bring more comfort to patients and healthcare professionals.
Group Chats and Calls
Group chats and video calls are necessary to allow a doctor to add their colleagues to an ongoing call with a patient for a quick, on-the-spot consultation. Doctors can also hop on a group call to review lab test results during a live chat.
Integration with EHR
It goes without saying that accurate patient history is a must for any healthcare organization. Being able to sync patient info and medical records gathered during remote consultations directly to an electronic health records system can save med personnel a lot of time.
Read more our telehealth EHR integration guide
VR for Telepsychiatry
Mental health sessions can be enhanced with a virtual settng that helps establish trust between specialists and patients.
Related: How to Create a Mental Health App
E-prescriptions
A telehealth app may incorporate an e-prescription component to expedite the process of prescribing meds and simplify prescription management.
Related: Pharmacy App Development Guide
Mobile Payments
To make the process of joining a call for patients as seamless as possible, you might need to integrate a payment gateway. That way, patients will be able to pay for the services right in the app, before a call. Many telemedicine apps implement this functionality via a web view to bypass Apple/Google commissions and allow patients to pay per visit or as a subscription (e.g., per month).
Integration with Peripheral IoT Devices
Certain medical specialties may benefit from connecting a telehealth app to a medical device like intraoral cameras used in teledentistry or other mobile devices/sensors. This option definitely helps providers come up with accurate diagnoses.
Related: IoT App Development: The Ultimate Guide
Integration with Healthkit and GoogleFit
To make sure doctors have a full understanding of a patient’s condition, it makes sense to integrate a telehealth app with Apple’s Healthkit and Google’s GoogleFit. These services supply all relevant patient health data.
Built-in Chatbot
Chatbots can be an excellent tool for triaging simple cases before a call and as a help desk alternative.
To learn more, we recommend reading our articles about chatbots in medicine and how to build your own chatbot.
Provider-Specific Options
You may want to include addional functionality for doctors, e.g., charts for easier disease management or a case management system.
Module for Medical Assistants
Most advanced telehealth apps sometimes include a separate UI for nurses, medical professionals, and other medical assistants that may join the call to update patient data, notes, and everything else that doctors can absolutely live without (for example, administrative tasks).
Related: Virtual Nurse App Development Guide
How Do I Build a Telehealth App Step by Step?
Are you ready for a detailed, step-by-step tutorial to building high-quality telemedicine applications? Buckle up, because we’re about to dive deep into the telemedicine app development process, exploring every critical aspect from choosing the right platform to deploying and maintaining your app. Here’s what you can expect:
-
-
- Step 1: Choose a platform (mobile/desktop/etc) – The first crucial decision in your journey.
- Step 2: Design the perfect telehealth app – Creating an intuitive and user-friendly experience is key.
- Step 3: Choose APIs you can use to integrate into your app – Let’s talk about the technical backbone of your telemedicine app.
- Step 4: Test your telemedicine app – Because nothing less than perfect will do.
- Step 5: Deploy and maintain your app – It’s not just about launching; it’s about ensuring long-term success.
-
Are you excited yet? Let’s get started and prep you for a meeting with consultants!
Week-by-Week Telehealth App Development Timeline
Weeks 1-2: Discovery & Planning
- Define HIPAA requirements
- Choose video API (Twilio vs Agora)
- Map user journeys for patients/doctors
- Security architecture planning
Weeks 3-4: Design Phase
- Patient app wireframes (15-20 screens)
- Doctor dashboard design (10-15 screens)
- Appointment flow prototyping
- HIPAA-compliant UI elements
Weeks 5-8: Backend Development
- Set up HIPAA-compliant cloud (AWS/Google)
- Implement authentication (2FA required)
- Video call infrastructure
- Database encryption setup
Weeks 9-12: Frontend Development
- React Native app development
- Doctor web portal
- Real-time chat implementation
- Payment gateway integration
Step 1: Choose a Platform
Typical timing: Weeks 1–2 (Discovery & Planning)
Before you commission your designers and start coding, you need to decide which platforms to custom develop your app for whether you’re building a fitness app, or a meditation app, etc. iOS and Android for mobile, web and native for desktop. Your target geography and app functions will direct your choices.
If you remember our recent article about making health apps for the iPhone, we discussed why an iOS-only approach works best for the USA, and an Android-first approach for the rest of the world.
For the sake of this article, we’re focusing on the US market. So, how do you approach developing a telemedicine platform?
Mobile: iOS or Android?
Have you considered support for iOS/Android?
The iPhone makes up for 55% of the total smartphone user base in the USA with Android accounting for the remaining 45%.
These statistics may sway you to build an iOS-only version of your telehealth app because iOS users are known to spend up to three times more than Android users. And the development of telehealth mobile app for Android may follow after iOS.
But at 45%, Android users are too many to be ignored, so you need to factor this into your long-term planning. In fact, when you think about telemedicine mobile app development, it’s clear that catering to both sides of the fence can really pay off in the long run.
Naturally, React Native is almost always the most sensible platform to begin with for healthcare application development, given the likely need to cater to both iOS and Android devices.
Related: Swift or React Native: Which to Choose?
Choosing the right platform for your mobile app
Desktop: Native or Web?
You will need a web app for patients who cannot access an iOS or Android device, as well as for physicians to manage their workflows and patient files.
The cost of building a web app and a native app is almost the same. In fact, a web app can be converted into a native desktop app that works on Mac, Windows, and Linux using tools like Electron. Slack is an example of software built with Electron. Another consideration on your list is mobile web – should the application be accessible through mobile browsers?
Choosing Between SaaS and Custom Build
A SaaS solution does not give you the liberty to personalize the front-end experience beyond a logo and name change. Other than that, the app is identical to all their other customers’ apps.
If you want to control exactly how your app looks and functions, you’ll need a custom-built solution. In this case, say, telenursing app development services from healthcare app development experts may come handy.
A custom mobile app is developed using open source or paid APIs. This gives you granular control over your entire app and helps to integrate it seamlessly with your existing infrastructure. By using TURN servers and protocols such as WebRTC to handle your videotelephony, we can create a telehealth platform that works just the way you want it.
If you’re debating white-label vs custom, jump to the decision guide in the White Label section.
Is SaaS Cheaper Than a Custom Build?
SaaS solutions typically support the business model based on a monthly subscription fee. They can be deployed relatively quickly because there is little to no programming involved. The monthly payment is usually adjusted according to user volumes. This is an overhead you have to maintain indefinitely.
SaaSs may initially appear to be the cheaper option, but it can become the more expensive choice once you outgrow the capabilities of your SaaSs product. When you reach that stage, you’ll be back searching for a custom solution to meet your growing business needs.
Also, you have no control as to when or what changes your SaaSs provider makes to your app. They can remove features and update policies on a whim. And because they have to support many clients, this may lead to some uncomfortable compromises for everyone.
Yes, a custom-built app may be more expensive in the short term because of development and maintenance costs, but you get more value out of it in the long run. As part of this strategy you’ll have to create a mobile telehealth app and a web dashboard for providers.
Carefully weigh the cost-to-benefit ratio and product-market fit before deciding which way to go. A custom-built app offers absolute authority over every aspect of your app, including branding.
Step 2: Design the Perfect Telehealth App
Typical timing: Weeks 3–4 (Design)
User Experience Design
The user experience design is the most critical aspect of the entire health app design phase.
Many entrepreneurs come up with great app ideas and build apps that work very well from a technical standpoint but end up failing because the user experience is out of touch with the target audience.
It is not enough to have the right technology. You need to understand the people you are trying to help.
The UX design stage is where this can be prevented.
You will be designing two sides of your app – a provider backend and a front-facing patient side.
Be sure to simplify the onboarding process as much as possible by limiting the number of screens to a maximum of three. Too much information and you could make it difficult for your users. The copy must be written in 3rd grade English. Everyone can understand that level of English. You’re not trying to impress users. You want them to do exactly as you say without second-guessing.
Time spent on every call will be charged, so strive to make the app as easy to use as possible. The provider and patient need to concentrate on the consultation, not trying to figure out how to navigate and use your app.
After your UX wireframes are completed, you need to set up a focus group and conduct user testing. Get user feedback, revise the UI design according to their recommendations. Repeat the process until you are satisfied.
Once this stage is complete, you’re ready for the next one – User Interface Design.
User Interface Design
The User Interface Design stage adds skin to the UX wireframes. Colors, buttons, fonts, and all other visual aspects of the app come to life in this stage of mobile application development.
Different colors and button sizes need to be tested. User behavior is affected by colors and the position of components on a screen. The UI must then be converted into a working prototype using a process similar to our rapid prototyping process and also subjected to user testing.
Like the UX stage, revisions must be made as needed until you are satisfied.
Please note that this is but a brief glimpse of the whole design process. For a more in-depth look, please read our 7-Step Ultimate Guide to Mobile App Design. I highly recommend that you check it out.
Step 3: Choose APIs You Can Use to Integrate Into Your App
Typical timing: Weeks 1–2 for selection, Weeks 5–12 for integration
Building a telehealth app in the absence of market-ready APIs can easily take 1 to 2 years. But with the components now readily available in the market, a telehealth app can be built in 3-6 months.
This doesn’t diminish the fact that it is still a very difficult and time-consuming task to make third-party APIs work as desired (make sure you work with a tech-savvy project manager). Let’s take a look at some of the leading architecture building blocks:
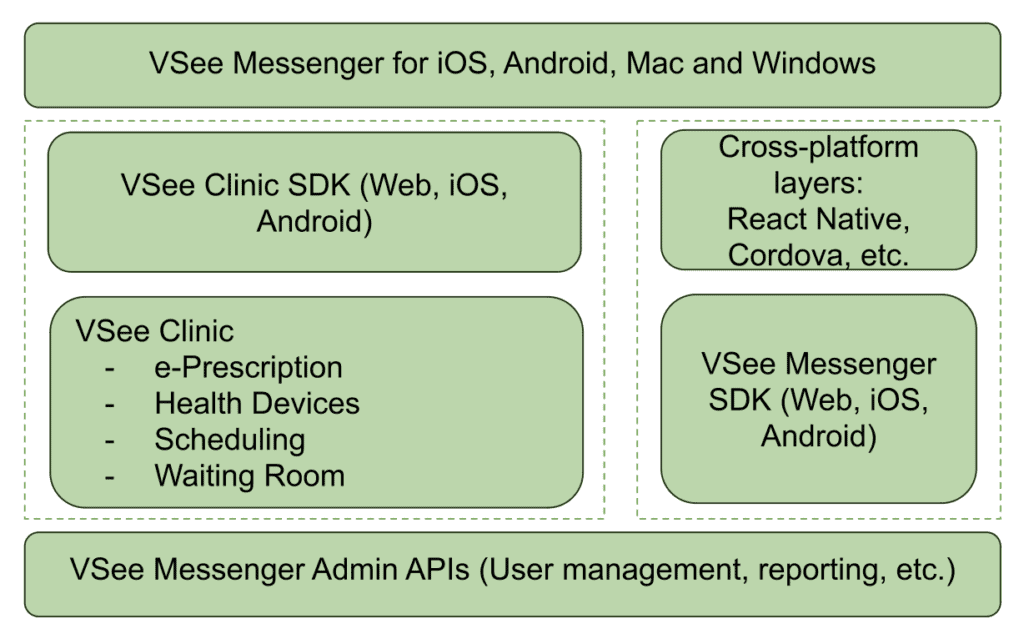
VSee SDK
VSee SDK is a rich telemedicine API that integrates end-to-end encrypted video calls into your mobile app for iOS and Android, as well as native apps on Mac and PC.
It’s HIPAA compliant and has its own server-client, so you don’t need to provision a server to set it up. It drastically reduces the technical workload, allowing you to focus on user experience and interface design.
Image credit: VSee
However, the drawback is that it’s not open source, and there’s a significant cost barrier to get the customizable codebase. Access to the codebase can cost as much as $20,000. Failure to get that would mean you have to settle for their SaaSs option, which provides no personalization besides a name and logo.
VIDYO
This API allows you to integrate real-time communication capabilities into your app on multiple platforms, including Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, and Android.
It has built-in text chat, so you don’t need to use a separate text chat API. The back-end also supports screen share as well as multiparty video calls for group video conferencing.
Vidyo’s not an open-source product. It offers minimal customization because they emphasize embedding their software into your app. That makes it similar to a SaaSs product with limitations to customization.
WebRTC
WebRTC is a free and open-source platform that enables real-time communication in web and native apps. It has simple APIs that have been optimized to transmit audio, video, and data. Supported browsers are Firefox, Opera, and Chrome on desktop and Android.
Native support is also available for Android and iOS. macOS and Windows are not supported.
The setup of this API is more involved than the others, but it’s very customizable.
OpenTok > Vonage
OpenTok is a cloud-based WebRTC platform. While WebRTC is an open-source, the software that powers OpenTok is not. With that being said, it offers all the customization potential you’d have on your own WebRTC deployment.
Image credit: Vonage Video API
Owned and developed by Vonage, OpenTok also allows you to integrate video, voice, text messaging, and screen sharing into your app on the web, iOS, Android, and Windows. It doesn’t support macOS.
OpenTok supports HIPAA-compliant app development. The development company building your app is responsible for configuring the app per HIPAA requirements and choosing the appropriate tech stack.
Twilio
Dr+ On Demand is powered by Twilio Programmable Video API. It works on all browsers without users installing any plugin and on iOS and Android.
It integrates with platform APIs like iOS CallKit, ARKit, and more. This makes it very versatile with many possible functionalities you can add to your app. It’s incredibly agile and can easily be scaled from starter to enterprise instantly.
Twilio boasts a lower latency than all other available platforms, claiming up to 50% better video quality.
Twilio also has APIs for SMS messaging, voice calls, text chat, email, fax, and even WhatsApp. Of all platforms, Twilio is the most robust and offers the best integration options.
Choosing Video APIs
Video APIs are one of those “looks cheap on a pricing page, gets expensive in production” choices — mostly because vendors bill differently (participant-minutes vs archive minutes vs flat per-provider plans) and because telehealth adds compliance overhead (BAAs, security configuration, and data retention). The quick table below is meant to help you sanity-check tradeoffs fast, then the two mini scenarios underneath show how the same product can land in a very different monthly range depending on call volume, average participants, and whether you record sessions.
Video API Comparison for Telehealth
|
API |
Cost (USD) |
HIPAA Compliant |
Setup Time |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Twilio Video |
$0.004 per participant-minute (Group Rooms). Recording: $0.004 per participant-minute. |
HIPAA-eligible with BAA + proper config |
~1–2 weeks |
Mature SDKs, global scale, predictable usage-based billing |
|
Agora (RTE) |
$3.99 / 1000 participant-minutes for HD video (≈ $0.00399 per participant-minute). First 10,000 min/month free. Recording: $0.99/1000 min. |
Yes with BAA + secure config |
~1 week |
Cost-effective MVPs + scaling when you want low list prices and a free tier |
|
Vonage Video API (OpenTok) |
$0.00410 per participant-minute. Recording (composed): ~$0.026 (SD) to $0.0363 (HD) per archive-minute (higher for FHD). |
Yes, but typically Enterprise + BAA |
~2–3 weeks |
Feature-heavy builds (broadcast, SIP, add-ons) where you accept “enterprise pricing gravity” |
|
VSee (SDK / platform) |
$0–$49 per provider/month (subscription; not per-minute). Enterprise: contact sales. |
Yes — BAA included |
Days–1 week |
Fast telehealth rollout (platform approach) when you want “telehealth features included,” not raw video primitives |
|
Custom WebRTC (self-managed) |
Infrastructure cost (servers + bandwidth + ops). Example from your notes: AWS egress ~$0.09/GB; cost scales with video bitrate + TURN usage. |
Self-managed (you own BAA/security/compliance posture) |
~4–6+ weeks (often months) |
Full control + bespoke requirements (but you pay in engineering time and ops complexity) |
Two quick sanity-check scenarios (monthly video + recording, list prices)
(Not quotes. Real pricing varies with discounts, regions, and recording modes.)
|
Vendor |
MVP clinic (500×20min, 2 ppl, no recording) |
Scaling (5,000×25min, 3 ppl avg, 20% recorded) |
What drives the bill |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Twilio |
~$80 |
~$1,800 |
Participant-minutes; recording scales linearly |
|
Agora |
~$40 (first 10k free) |
~$1,530 |
Lower list price + separate (cheap) recording rate |
|
Vonage |
~$82 |
~$3,487–$4,260 |
Recording/composed archive can dominate total cost |
|
VSee |
$0–$29 |
$49/provider/mo (× providers) |
Predictable budgeting; not usage-based |
|
Custom WebRTC |
~$20–$40 (infra only) |
~$500–$1,000+ (infra only) |
Bandwidth + TURN + ops/support become the “real bill” |
What this means in practice (3 bullets):
-
If you don’t record, Twilio/Agora/Vonage are in the same ballpark; your choice is mostly SDK maturity + ops preference.
-
If you do record, Vonage can get expensive fast (recording mode matters more than the base call rate).
-
“Custom” looks cheap on infra but you pay in engineering + ongoing ops (monitoring, scaling, compliance, troubleshooting).
(All costs USD, as-of late 2025. Actual bills may vary with volume discounts, regional rates, and contract terms.)
Decision Guide: Which Video Stack Should You Pick for Telehealth?
(Rule of thumb based on vendor list pricing + your scenarios; real pricing can change with BAAs, regions, volume discounts, and recording mode.)
1) Are you trying to ship a compliant telehealth experience fast (days → 1 week) with “telehealth features included,” not raw video primitives?
→ Yes: VSee (platform/subscription approach; BAA included; per-provider pricing model)
→ No / you want raw video API building blocks: go to #2
2) Do you need full control / bespoke requirements that don’t fit vendor constraints (custom media routing, unusual topology, specialized infra/security posture), and you’re okay owning ops + compliance?
→ Yes: Custom WebRTC (self-managed) (expect longer setup + ongoing ops)
→ No: go to #3
3) Will recording be a meaningful part of the product (e.g., >10–20% of visits recorded, or you need composed recordings)?
→ Yes: go to #4
→ No (mostly live visits): go to #5
4) Recording-heavy path
-
Need recording, but want to keep list-price costs down for an MVP or early scale?
→ Agora (lower list price per participant-minute; separate lower recording rate in your table)
-
Need a feature-heavy “enterprise add-ons” ecosystem and accept enterprise pricing gravity?
→ Vonage (but watch recording/composed archive costs—your scenario shows it can dominate total cost)
-
Need predictable, mature SDKs and broad ecosystem; recording costs are acceptable and you value reliability + docs
→ Twilio
5) Mostly live visits (little/no recording)
Is your top priority “mature SDKs + global scale + predictable usage-based billing”?
→ Yes: Twilio
→ No / you’re cost-sensitive and want a lower list price + free tier for early usage: Agora
→ No / you specifically want feature-heavy enterprise add-ons (broadcast/SIP/etc.) and can tolerate longer setup: Vonage
What’s your pricing model preference?
-
If you hate per-minute variability and want “per provider” budgeting → VSee
-
If your usage is uncertain and you want usage-based alignment → Twilio / Agora / Vonage
-
If you want infra-based costs and accept engineering/ops complexity → Custom WebRTC
Acuity – Scheduling
Acuity has been designed to support the healthcare industry’s needs and, as such, is HIPAA-compliant. You’ll need a Powerhouse plan for you to enter into a BAA with Acuity Scheduling.
How do you or your development team select the right APIs?
This depends on your choice of platform and what functions you need. The best combination, however, is using React Native as your platform, Twilio — for video and chat. The chat must be encrypted with Virgil Security’s end-to-end encryption SDK.
Step 4: Test Your Telemedicine App
Typical timing: Continuous (Weeks 5–12) + final regression in Week 12
We can’t stress enough how important that stage is. Making sure your app works flawlessly is a huge milestone in the telehealth app development journey. You should have your app developers execute peer code reviews. At the same time, the QA team carries out unit tests on various devices.
Even though a properly setup QA process implies frequent testing after each sprint, do plan for a final quality assurance round that includes regression testing and covers everything you’ve already tested during previous sprints. We recommend performing stress testing early on during telemedicine platform development and certainly before the launch to see if the app can hold an inflow of new users.
Related: Complete Guide to QA Testing
Step 5: Deploy and Maintain Your App
Typical timing: Week 12+ (release + monitoring)
Finally, once the app has been developed, it’s time to move it to a live environment and into the app stores where customers can download it. Now you’re fully ready for starting a telemedicine app.
IOS and Android receive updates every year. It’s essential to update the app accordingly to make sure it continues providing the best user experience and vigilant data security.
That’s the gist of the development process for creating a telemedicine application.
Also Read: How to build a medical startup and succeed in healthcare
White Label Telemedicine Solutions
If you desperately need to deploy a telehealth solution, ready-made telehealth solutions come to the rescue. There are solutions on the market that include AI options to help you implement the most critical features of virtual care:
- user authentication
- scheduling
- video calling
- voice calling
- real-time chat
Such off-the-shelf customizable components can trim your time to market from 9 months to just a 1-2 months, depending on the level of customization you need.
These components are designed and developed to provide you with:
- A sleek and intuitive UI/UX for both web and mobile platforms
- Effortless compatibility with each components
- Seamless incorporation into popular tech stacks (e.g., NodeJS, ReactJS, ReactNative)
- Consistent and dependable performance at scale
- HIPAA compliance
- Robust security measures/ data protection
- Quality control
- Features that meet the majority of user needs and match those of leading SaaS providers
- Fully customizable user experience and functionality
White-label telemedicine platforms can be the fastest way to get to a real pilot—especially if you’re validating demand or need a working product before you invest in a fully custom build. The tradeoff is flexibility: once you need specialty workflows, deep integrations, or a differentiated patient experience, you may end up fighting the platform instead of building your own. Use the quick decision guide below to sanity-check which path fits your situation.
Decision Guide: Should You build Custom or Use White-Label?
(Rule of thumb—exact breakpoints vary by specialty, integrations, and compliance scope.)
1) Do you need to launch in ≤ 60 days (pilot/MVP)?
→ Yes: Start with white-label
→ No: Go to #2
2) Annual patient visits under ~10,000?
→ Yes: White-label is often the fastest ROI path (validate demand and workflows first)
→ No: Go to #3
3) Do you need custom workflows? (e.g., specialty intake logic, triage/routing rules, care plans, role-based task queues, complex billing rules beyond standard scheduling + video)
→ Yes: Custom build is typically required
→ No: Go to #4
4) Do you need deep integrations now? (EHR/EMR, SSO, payer/eligibility, enterprise scheduling, device/RPM feeds)
→ Yes: Lean custom (or expect enterprise-grade white-label pricing + constraints)
→ No: Go to #5
5) Is your budget comfortable in the ~$150k+ range for v1? (Rule of thumb.)
→ Yes: Custom build for control, differentiation, and long-term flexibility
→ No: Start with white-label, prove traction, then migrate to custom once requirements and ROI are clear
Rule-of-thumb cost note: White-label plans often start in the hundreds to low-thousands per month, but pricing can rise quickly with provider count, usage, integrations, security/compliance add-ons, and support tiers.
How Much Does it Cost to Build a Telehealth App?
The cost of developing a telehealth app may vary from US$80,000 and all the way to US$349,000, depending on its complexity. Teladoc-like app development will easily run into millions of dollars because it’s a huge platform for virtually all platforms and lots of APIs.
Telehealth App Development Cost Breakdown 2025
|
Feature Set |
Development Time |
Cost Range |
Monthly Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Basic MVP (video + chat) |
3–4 months |
$80,000–$120,000 |
$2,000–$3,000 |
|
Standard (+ scheduling, payments) |
4–6 months |
$120,000–$180,000 |
$3,000–$5,000 |
|
Advanced (+ EHR, RPM, AI) |
6–9 months |
$180,000–$300,000 |
$5,000–$8,000 |
|
Enterprise (multi-platform) |
9–12 months |
$300,000–$500,000 |
$8,000–$15,000 |
On the lower end, we are talking cross-platform mobile apps that reuse as much as possible from a rather simple web telemedicine app. Also, remember that no-code telehealth app development is a perfect shortcut that saves a lot of money and expedites time to market. This approach will help you keep the telemedicine app development cost on a lower side.
And on the higher end, we mean an advanced web platform with native mobile apps specifically optimized for smartphones and tablets. How long it takes to develop your app will depend on various factors like the features needed, cross platform vs native, where in the development stage you are and more.
Telehealth Development Approaches Compared
| Approach | Time to Launch | Total Cost Year 1 | Customization | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doxy.me white-label | 1–2 weeks | $20,000–$40,000 | Minimal | Quick launch |
| Custom React Native | 4–6 months | $150,000–$200,000 | Full | Unique features |
| Hybrid (APIs + custom) | 2–3 months | $80,000–$120,000 | Moderate | Balance |
| No-code platforms | 2–4 weeks | $10,000–$30,000 | Limited | Testing market |
Hopefully, this info helps you answer “How much does it cost to develop a telemedicine app?” and determine the right budget.
Also read: The Health App Founder’s Dilemma: Achieving traction without over-investing
How Topflight Fast-Tracks Telehealth App Success
Telehealth isn’t just “Zoom for doctors” anymore—it’s remote patient monitoring, computer-vision-powered rehab, and asynchronous consults that slot into a clinician’s day like email. Topflight has shipped that full spectrum, from RTHM’s long-COVID ecosystem that marries wearables with provider dashboards to Allheartz’s computer-vision RTM platform that cuts in-person check-ups by up to 50 % and slashes clerical work 80 %. We treat every telehealth build as a revenue engine, not a science project—so founders get to proof-of-value before their runway blinks red.
$188 million+ in follow-on funding has landed in our clients’ bank accounts, underscoring that VCs reward apps that ship fast and clear the HIPAA, FDA, and payer gauntlets on day one.
Why telehealth teams pick Topflight
-
Async & RPM ready-made – Video annotation, SMART-on-FHIR data pulls, and device integrations come as drop-ins, so you start clinical pilots in weeks, not quarters.
-
Computer-vision expertise – Pose-estimation models (MoveNet, TensorFlow) already battle-tested in production rehab workflows.
-
Compliance baked in – End-to-end encryption, 2-factor auth, and PHI-safe cloud pipelines mean no “security tax” right before launch.
-
Built-for-fundraising UX – The metrics that matter—reduced visits, injury prevention, provider time saved—are wired into dashboards from sprint one, arming you with investor-grade traction data.
Time to Make a Telemedicine App
Now that you know how to develop a telehealth app and what it costs, it’s time to custom build your app. At TopFlight Apps, we specialize in building health apps for iOS, Android, and the web. We’ve proven our salt’s worth and helped health startups like Xzevn, Smarter Symptom Tracker, and RingRx create successful businesses by building robust apps that meet and exceed their needs.
Do you have a telehealth app project? We’d like to help you with it. Explore our telemedicine website development services and get in touch here. We’re happy to help you build your own telemedicine application.
Related Articles:
[This blog was originally published in June 2021 but has been updated for more recent content]
Frequently Asked Questions
What does an average telemedicine app consist of?
Typically: a patient app (mobile or web), a clinician app (mobile or web), an admin console, and a secure back end with a database. The core stack usually also includes secure video or audio, messaging, scheduling, notifications, audit logging, and role-based access controls.
What is the minimum feature set for a telehealth MVP?
A practical MVP usually includes: patient onboarding and consent, provider profiles, appointment scheduling, secure video or audio visits, secure messaging, basic documentation notes, and an admin panel for user and content management. If you handle any PHI, include encryption in transit and at rest, access controls, and audit logs from day one.
How long does it take to develop a telemedicine app?
Most MVPs land in the 3 to 6 month range, depending on the scope of scheduling, payments, roles and permissions, and the complexity of the visit workflows. EHR integration, RPM device connectivity, and multi-location administration can extend timelines materially.
What drives telehealth development cost up the fastest?
The biggest multipliers are integrations and operational complexity: EHR connectivity, insurance and billing workflows, RPM devices and alerting, multi-tenant setups for multiple clinics, and advanced security controls with formal audits and documentation. Video is rarely the hard part; everything around the visit usually is.
Do I need FDA approval for my telehealth app?
Only if you are making diagnostic claims. General consultation apps do not need FDA approval, but apps with AI diagnostics or medical device integration do.
How long does HIPAA compliance add to development?
Adds 3 to 4 weeks for basic compliance, 6 to 8 weeks for full security audits and documentation.
Can I use Zoom for telehealth?
No. Zoom for Healthcare (with BAA) costs $200 per month minimum. Consumer Zoom violates HIPAA.
Can I develop a telehealth solution as a mobile app without a web component?
Yes, but most real-world deployments still need at least a lightweight web layer for administration (user management, content and settings, audit review, support workflows). Clinicians also often prefer a web view for documentation and back-office tasks, even if visits happen on mobile.
Can I develop a cross-platform telemedicine app?
Yes. Cross-platform can work well for many telehealth apps, especially when you prioritize speed and consistency across iOS and Android. The main watch-out is real-time media quality and device-level capabilities; if you need top-tier video performance, complex camera flows, or deep hardware usage, native builds are often safer.